Candidatus Alkanophaga archaea from Guaymas Basin hydrothermal vent sediment oxidize petroleum alkanes
- PMID: 37264141
- PMCID: PMC10322722
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-023-01400-3
Candidatus Alkanophaga archaea from Guaymas Basin hydrothermal vent sediment oxidize petroleum alkanes
Abstract
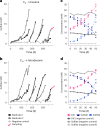
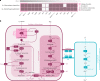
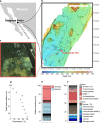
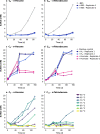
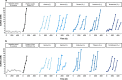
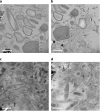
Methanogenic and methanotrophic archaea produce and consume the greenhouse gas methane, respectively, using the reversible enzyme methyl-coenzyme M reductase (Mcr). Recently, Mcr variants that can activate multicarbon alkanes have been recovered from archaeal enrichment cultures. These enzymes, called alkyl-coenzyme M reductase (Acrs), are widespread in the environment but remain poorly understood. Here we produced anoxic cultures degrading mid-chain petroleum n-alkanes between pentane (C5) and tetradecane (C14) at 70 °C using oil-rich Guaymas Basin sediments. In these cultures, archaea of the genus Candidatus Alkanophaga activate the alkanes with Acrs and completely oxidize the alkyl groups to CO2. Ca. Alkanophaga form a deep-branching sister clade to the methanotrophs ANME-1 and are closely related to the short-chain alkane oxidizers Ca. Syntrophoarchaeum. Incapable of sulfate reduction, Ca. Alkanophaga shuttle electrons released from alkane oxidation to the sulfate-reducing Ca. Thermodesulfobacterium syntrophicum. These syntrophic consortia are potential key players in petroleum degradation in heated oil reservoirs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Claypool GE, Kvenvolden KA. Methane and other hydrocarbon gases in marine sediment. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1983;11:299–327. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.11.050183.001503. - DOI
-
- Simoneit BRT. Petroleum generation, an easy and widespread process in hydrothermal systems: an overview. Appl. Geochem. 1990;5:3–15. doi: 10.1016/0883-2927(90)90031-Y. - DOI
-
- Kissin YV. Catagenesis and composition of petroleum: origin of n-alkanes and isoalkanes in petroleum crudes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1987;51:2445–2457. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90296-1. - DOI
-
- Aeckersberg F, Bak F, Widdel F. Anaerobic oxidation of saturated hydrocarbons to CO2 by a new type of sulfate-reducing bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 1991;156:5–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00418180. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

