Reverse transcription-free digital-quantitative-PCR for microRNA analysis
- PMID: 37264955
- PMCID: PMC10318481
- DOI: 10.1039/d3an00351e
Reverse transcription-free digital-quantitative-PCR for microRNA analysis
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding RNA sequences that regulate many biological processes and have become central targets of biomedical research. However, their naturally low abundances in biological samples necessitates the development of sensitive analytical techniques to conduct routine miRNA measurements in research laboratories. Digital PCR has the potential to meet this need because of its single-molecule detection capabilities, but PCR analyses of miRNAs are slowed by the ligation and reverse transcription steps first required to prepare samples. This report describes the development of a method to rapidly quantify miRNA in digital microwell arrays using base-stacking digital-quantitative-PCR (BS-dqPCR). BS-dqPCR expedites miRNA measurements by eliminating the need for ligation and reverse transcription steps, which reduces the time and cost compared to conventional miRNA PCR analyses. Under standard PCR thermocycling conditions, digital signals from miRNA samples were lower than expected, while signals from blanks were high. Therefore, a novel asymmetric thermocycling program was developed that maximized on-target signal from miRNA while minimizing non-specific amplification. The analytical response of BS-dqPCR was then evaluated over a range of miRNA concentrations. The digital PCR dimension increased in signal with increasing miRNA copy numbers. When the digital signal saturated, the quantitative PCR dimension readily discerned miRNA copy number differences. Overall, BS-dqPCR provides rapid, high-sensitivity measurements of miRNA over a wide dynamic range, which demonstrates its utility for routine miRNA analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

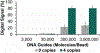



Similar articles
-
Multiplexed miRNA and Protein Analysis Using Digital Quantitative PCR in Microwell Arrays.Anal Chem. 2024 Jan 23;96(3):1371-1379. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05213. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38183281 Free PMC article.
-
Precise Quantitation of MicroRNA in a Single Cell with Droplet Digital PCR Based on Ligation Reaction.Anal Chem. 2016 Dec 6;88(23):11384-11389. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b01225. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Anal Chem. 2016. PMID: 27800678
-
Steps to achieve quantitative measurements of microRNA using two step droplet digital PCR.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 16;12(11):e0188085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188085. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29145448 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in microRNA detection.Analyst. 2018 Apr 16;143(8):1758-1774. doi: 10.1039/C7AN02001E. Analyst. 2018. PMID: 29560992 Review.
-
Current Methods of microRNA Analysis.Klin Onkol. 2018 Winter;31(Suppl 2):93-101. doi: 10.14735/amko20182S93. Klin Onkol. 2018. PMID: 31023031 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Selective miRNA quantitation with high-temperature thermal gel electrophoresis.Anal Chim Acta. 2023 Sep 22;1275:341605. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2023.341605. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Anal Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 37524470 Free PMC article.
-
Exonuclease-III Assisted Signal Cycle Integrating with Self-Priming Mediated Chain Extension for Sensitive and Reliable MicroRNA Detection.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 8;10(6):6228-6233. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c11417. eCollection 2025 Feb 18. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39989823 Free PMC article.
-
Microinjection molded microwell array-based portable digital PCR system for the detection of infectious respiratory viruses.Nano Converg. 2025 Mar 21;12(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40580-025-00482-5. Nano Converg. 2025. PMID: 40119017 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexed miRNA and Protein Analysis Using Digital Quantitative PCR in Microwell Arrays.Anal Chem. 2024 Jan 23;96(3):1371-1379. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c05213. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38183281 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Biopsy and Multidisciplinary Treatment for Esophageal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 9;17(2):196. doi: 10.3390/cancers17020196. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857978 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shen L; Gan M; Li Q; Wang J; Li X; Zhang S; Zhu L, MicroRNA-200b regulates preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation by targeting KLF4. Biomed. Pharmacother 2018, 103, 1538–1544. - PubMed
-
- Chen J-Q; Papp G; Szodoray P; Zeher M, The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev 2016, 15 (12), 1171–1180. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

