Interaction between apical periodontitis and systemic disease (Review)
- PMID: 37264964
- PMCID: PMC10249585
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5263
Interaction between apical periodontitis and systemic disease (Review)
Abstract
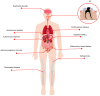
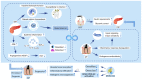
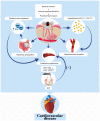
Apical periodontitis is an oral common inflammatory disease initiated by infection of pulp chamber and is characterized by destruction and resorption of the periapical bone. As a local infection, pathogens and their products in periapical tissues, as well as inflammatory cytokines produced in periapical lesions, enter the blood circulation, triggering systemic immune responses and leading to the pathogenesis of various types of systemic disease. Therefore, apical periodontitis might be associated with systemic disease rather than solely simple local oral disease. In addition, the existence of a hyperinflammatory state in certain patients with chronic inflammation‑related disorder may affect the progression or prognosis of apical periodontitis. However, the association and potential mechanisms between apical periodontitis and systemic diseases remain unclear. An in‑depth understanding of the association between apical periodontitis and systemic disease will be useful for both dentists and physicians to eliminate the possible risk factors and promote the healing of apical periodontitis and systemic disease. Thus, the aim of the present review is to introduce the potential relationship between apical periodontitis and systemic disease.
Keywords: apical periodontitis; association; inflammation; microbiota; systemic disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Two-Way Communication Between Apical Periodontitis and Various Systemic Disorders: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2025 Mar 30;17(3):e81482. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81482. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40308406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes mellitus and inflammatory pulpal and periapical disease: a review.Int Endod J. 2013 Aug;46(8):700-9. doi: 10.1111/iej.12072. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Int Endod J. 2013. PMID: 23442003 Review.
-
Endodontic medicine: connections between apical periodontitis and systemic diseases.Int Endod J. 2015 Oct;48(10):933-51. doi: 10.1111/iej.12507. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Int Endod J. 2015. PMID: 26174809 Review.
-
NLRP12 Attenuates Inflammatory Bone Loss in Experimental Apical Periodontitis.J Dent Res. 2019 Apr;98(4):476-484. doi: 10.1177/0022034518820289. Epub 2019 Jan 25. J Dent Res. 2019. PMID: 30681895
-
Monospecies Bacteria-Induced Chronic Apical Periodontitis Triggers the Aortic Inflammatory Response Via Modulation of Systemic Inflammation and Lipid Metabolism.Lab Invest. 2025 Apr;105(4):104095. doi: 10.1016/j.labinv.2025.104095. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Lab Invest. 2025. PMID: 39826684
Cited by
-
Effects of psychological intervention combined with education on psychological resilience and healthy behavior of patients with pulp disease.World J Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 19;15(4):100929. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.100929. eCollection 2025 Apr 19. World J Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40309598 Free PMC article.
-
Association between apical periodontitis and brain inflammation: a systematic review from animals and human studies.Odontology. 2025 Feb 27. doi: 10.1007/s10266-025-01069-6. Online ahead of print. Odontology. 2025. PMID: 40011389 Review.
-
Comparative outcomes of endodontically treated teeth versus dental implant-supported prostheses: a systematic review.Acta Odontol Scand. 2025 Jun 24;84:386-396. doi: 10.2340/aos.v84.43871. Acta Odontol Scand. 2025. PMID: 40552466 Free PMC article.
-
Association between dental diseases and oral hygiene care and the risk of vertebral fracture: a nationwide cohort study.Osteoporos Int. 2024 Apr;35(4):635-644. doi: 10.1007/s00198-023-06983-5. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Osteoporos Int. 2024. PMID: 38095696
-
Effects of N-acetyl-L-cysteine polysulfides on periodontitis in a mouse model.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Aug;11(8):e959. doi: 10.1002/iid3.959. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37647428 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

