Biomarkers of lung alveolarization and microvascular maturation in response to intermittent hypoxia and/or early antioxidant/fish oil supplementation in neonatal rats
- PMID: 37265429
- PMCID: PMC10463793
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.26495
Biomarkers of lung alveolarization and microvascular maturation in response to intermittent hypoxia and/or early antioxidant/fish oil supplementation in neonatal rats
Abstract
Objective: Extremely preterm infants experience frequent intermittent hypoxia (IH) episodes during oxygen therapy which causes significant damage to the lungs and curtails important signaling pathways that regulate normal lung alveolarization and microvascular maturation. We tested the hypothesis that early supplementation with fish oil and/or antioxidants in rats exposed to neonatal IH improves expression of lung biomarkers of alveolarization and microvascular maturation, and reduces IH-induced lung injury.
Study design/methods: From birth (P0) to P14, rat pups were exposed to room air (RA) or neonatal IH during which they received daily oral supplementation with either: (1) olive oil (OO) (control); (2) Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in OO; (3) fish oil; (4) glutathione nanoparticles (nGSH); or (5) fish oil +CoQ10. At P14 pups were placed in RA until P21 with no further treatment. RA controls were similarly treated. Lung growth and alveolarization, histopathology, apoptosis, oxidative stress and biomarkers of alveolarization and microvascular maturation were determined.
Results: Neonatal IH was associated with reduced lung weights and severe histopathological outcomes. These effects were curtailed with fish oil and nGSH. nGSH was also protective against apoptosis, while CoQ10 prevented IH-induced ROS production. Of all treatments, nGSH and CoQ10 + fish oil-induced vascular endothelial growth factor165 and CD31 (Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1), which are associated with angiogenesis. CoQ10 + fish oil improved alveolarization in RA and IH despite evidence of hemorrhage.
Conclusions: The benefits of nGSH and CoQ10 + fish oil suggest an antioxidant effect which may be required to curtail IH-induced lung injury. Further clinical assessment of the effectiveness of nGSH is warranted.
Keywords: alveolarization; glutathione nanoparticles; neonatal intermittent hypoxia; tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases; vascular endothelial growth factor.
© 2023 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

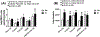
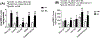
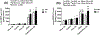
Similar articles
-
Biomarkers of growth and carbohydrate metabolism in neonatal rats supplemented with fish oil and/or antioxidants during intermittent hypoxia.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2023 Feb;68:101513. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2022.101513. Epub 2022 Nov 5. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2023. PMID: 36427361
-
Neonatal intermittent hypoxia, fish oil, and/or antioxidant supplementation on gut microbiota in neonatal rats.Pediatr Res. 2022 Jul;92(1):109-117. doi: 10.1038/s41390-021-01707-z. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Pediatr Res. 2022. PMID: 34455420 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of coenzyme Q10 or fish oil for prevention of intermittent hypoxia-induced oxidative injury in neonatal rat lungs.Respir Res. 2021 Jul 5;22(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01786-w. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 34225702 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants and/or fish oil reduce intermittent hypoxia-induced inflammation in the neonatal rat terminal ileum.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2021 Aug;155:106565. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2021.106565. Epub 2021 May 26. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2021. PMID: 34051366
-
Effects of omega 3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants, and/or non-steroidal inflammatory drugs in the brain of neonatal rats exposed to intermittent hypoxia.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2021 Aug;81(5):448-460. doi: 10.1002/jdn.10120. Epub 2021 May 25. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33969544
References
-
- Martin RJ, Di Fiore JM, Macfarlane PM, Wilson CG. Physiologic basis for intermittent hypoxic episodes in preterm infants. Adv Exp Med Biol 2012;758:351–358. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

