Bilateral Divergent Fracture Dislocations in a COVID-19 Patient Following a Hyponatremia-Induced Seizure
- PMID: 37265532
- PMCID: PMC10231924
Bilateral Divergent Fracture Dislocations in a COVID-19 Patient Following a Hyponatremia-Induced Seizure
Abstract
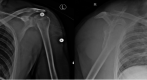
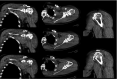
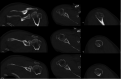
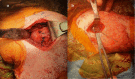
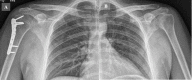
Bilateral divergent fracture dislocations of the shoulder are very rare. Caution with regards to seizure development in COVID-19 patients must be taken to avoid such injuries. This is the case of a male COVID-19 patient who sustained hyponatremia-induced seizure that resulted in bilateral divergent shoulder fracture dislocations. The patient suffered a lesser tuberosity fracture on his left shoulder which was posteriorly dislocated, and a greater tuberosity fracture on his right, which was anteriorly dislocated. The patient underwent bilateral open reduction and internal fixation, with suture anchor fixation for the lesser tuberosity fracture on the left side, and a proximal humerus locking plate for the greater tuberosity fracture on the right side. Education on postoperative complications and expectations were provided to the patient.
Keywords: Greater tuberosity; Lesser tuberosity; Locking plate; Suture anchor fixation.
Conflict of interest statement
JAA would like to disclose royalties from: DJO GLOBAL, ZIMMER-BIOMET, SMITH AND NEPHEW, STRYKER, GLOBUS MEDICAL, INC.; research support from as a PI from: LIMA CORPORATION - ITALY, ORTHOFIX, ARTHREX, OREF; royalties, financial or material support from: WOLTERS KLUWER; and board member/committee appointments for: AMERICAN SHOULDER AND ELBOW SOCIETY, PACIRA.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
