Pretreatment Vitamin D Concentrations Do Not Predict Therapeutic Outcome to Anti-TNF Therapies in Biologic-Naïve Patients With Active Luminal Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 37265586
- PMCID: PMC10231451
- DOI: 10.1093/crocol/otad026
Pretreatment Vitamin D Concentrations Do Not Predict Therapeutic Outcome to Anti-TNF Therapies in Biologic-Naïve Patients With Active Luminal Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Background and aims: Vitamin D has a regulatory role in innate and adaptive immune processes. Previous studies have reported that low pretreatment vitamin D concentrations are associated with primary non-response (PNR) and non-remission to anti-TNF therapy. This study aimed to assess whether pretreatment 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations predicted PNR and non-remission to infliximab and adalimumab in patients with active luminal Crohn's disease.
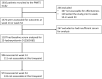
Methods: 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations were measured in stored baseline samples from 659 infliximab- and 448 adalimumab-treated patients in the Personalised Anti-TNF Therapy in Crohn's disease (PANTS) study. Cut-offs for vitamin D were deficiency <25 nmol/L, insufficiency 25-50 nmol/L, and adequacy/sufficiency >50 nmol/L.
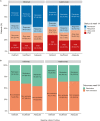
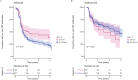
Results: About 17.1% (189/1107; 95% CI, 15.0-19.4) and 47.7% (528/1107; 95% CI, 44.8-50.6) of patients had vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency, respectively. 22.2% (246/1107) of patients were receiving vitamin D supplementation. Multivariable analysis confirmed that sampling during non-summer months, South Asian ethnicity, lower serum albumin concentrations, and non-treatment with vitamin D supplementation were independently associated with lower vitamin D concentrations. Pretreatment vitamin D status did not predict response or remission to anti-TNF therapy at week 14 (infliximab Ppnr = .89, adalimumab Ppnr = .18) or non-remission at week 54 (infliximab P = .13, adalimumab P = .58). Vitamin D deficiency was, however, associated with a longer time to immunogenicity in patients treated with infliximab, but not adalimumab.
Conclusions: Vitamin D deficiency is common in patients with active Crohn's disease. Unlike previous studies, pretreatment vitamin D concentration did not predict PNR to anti-TNF treatment at week 14 or nonremission at week 54.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; IBD; PANTS; vitamin D.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Crohn's & Colitis Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
S.L. reports nonfinancial support from Pfizer outside the submitted work. N.A.K. reports grants from F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, grants from Biogen Inc, grants from Celltrion Healthcare, grants from Galapagos NV, nonfinancial support from Immundiagnostik, grants and nonfinancial support from AbbVie, grants and personal fees from Celltrion, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Janssen, personal fees from Takeda, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Dr Falk, outside the submitted work. T.A. reports grants and nonfinancial support from F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, grants from Biogen Inc, grants from Celltrion Healthcare, grants from Galapagos NV, nonfinancial support from Immundiagnostik, personal fees from Biogen inc, grants and personal fees from Celltrion Healthcare, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Immundiagnostik, personal fees from Takeda, personal fees from ARENA, personal fees from Gilead, personal fees from Adcock Ingram Healthcare, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Genentech, nonfinancial support from Tillotts, outside the submitted work. J.R.G. reports grants from F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, grants from Biogen Inc, grants from Celltrion Healthcare, grants from Galapagos NV, nonfinancial support from Immundiagnostik, outside the submitted work. The following authors have nothing to declare: N.C., R.S., C.R., R.N., T.J.M., C.B., B.H., and M.B.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
