Pre-diagnostic blood biomarkers for adult glioma
- PMID: 37265788
- PMCID: PMC10229864
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1163289
Pre-diagnostic blood biomarkers for adult glioma
Abstract
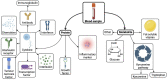
Glioma is one of the most common malignant primary brain tumours in adults, of which, glioblastoma is the most prevalent and malignant entity. Glioma is often diagnosed at a later stage of disease progression, which means it is associated with significant mortality and morbidity. Therefore, there is a need for earlier diagnosis of these tumours, which would require sensitive and specific biomarkers. These biomarkers could better predict glioma onset to improve diagnosis and therapeutic options for patients. While liquid biopsies could provide a cheap and non-invasive test to improve the earlier detection of glioma, there is little known on pre-diagnostic biomarkers which predate disease detection. In this review, we examine the evidence in the literature for pre-diagnostic biomarkers in glioma, including metabolomics and proteomics. We also consider the limitations of these approaches and future research directions of pre-diagnostic biomarkers for glioma.
Keywords: early detection; glioblastoma; glioma; liquid biomarkers; pre-diagnostic.
Copyright © 2023 Andrews, Davies, Herbert and Kurian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources