Case report: Neuroendocrine breast carcinoma with a germline EGFR T790M mutation
- PMID: 37265791
- PMCID: PMC10230275
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1176868
Case report: Neuroendocrine breast carcinoma with a germline EGFR T790M mutation
Abstract
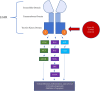
Background: The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) p.Thr790Met (T790M) mutation was discovered as a resistance mechanism in patients with lung cancer treated with first- and second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Further studies revealed the EGFR T790M mutation in treatment-naive non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) and as a rare germline mutation strongly associated with NSCLC. Somatic EGFR T790M mutations have been reported in a limited population of patients with triple-negative breast cancer. There are no previous reports of a germline EGFR T790M mutation found in a patient with breast cancer.
Case presentation: We present a rare case of a 42-year-old woman with a rapidly progressing 8 cm mass in the right lateral breast. An additional right breast mass with multiple lymph nodes characteristic or suspicious of metastasis was found. Ultrasound-guided biopsy showed high-grade, poorly differentiated invasive neuroendocrine carcinoma of the right breast and metastatic carcinoma of a right axillary lymph node. Genetic testing revealed a germline EGFR T790M mutation. The patient underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy, right mastectomy with lymph node dissection, adjuvant radiation to the right chest wall and axilla, and adjuvant chemotherapy.
Conclusion: This is the first reported case of a patient with high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma, triple-negative breast cancer and a germline EGFR T790M mutation. Further investigation is needed to find a possible correlation between the cancer in this patient and her mutation. Since there are no current guidelines, further research is also needed to define screening protocols for patients with germline EGFR T790M mutations. Additional treatment options and cancer risk could also be found with further research, which would benefit all patients with a germline EGFR T790M mutation.
Keywords: EGFR mutation; chemotherapy; germline EGFR T790M mutation; neuroendocrine breast cancer; triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Copyright © 2023 Sagan, Rothstein, Jambunathan, Hadziahmetovic, Antoniolli and Rashid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Significant Benefits of Osimertinib Against Adenosquamous Carcinoma Harboring Germline T790M Mutation.Oncologist. 2020 Oct;25(10):826-832. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0938. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32367600 Free PMC article.
-
Two case reports of non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring acquired EGFR T790M-cis-C797S benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitor combined with platinum-based doublet chemotherapy.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jun;10(12):719. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2436. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35845537 Free PMC article.
-
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR / HER-1) gatekeeper mutation T790M is present in European patients with early breast cancer.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 12;10(8):e0134398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134398. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26267891 Free PMC article.
-
Osimertinib: A third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor for treatment of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer with the acquired Thr790Met mutation.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018 Jul;24(5):379-388. doi: 10.1177/1078155217712401. Epub 2017 May 31. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2018. PMID: 28565936 Review.
-
Maximizing the Clinical Benefit of Anthracyclines in Addition to Taxanes in the Adjuvant Treatment of Early Breast Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Aug 10;35(23):2600-2603. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.5960. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28661760 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary neuroendocrine tumor of the breast: A case report.Oncol Lett. 2024 Nov 27;29(2):79. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14825. eCollection 2025 Feb. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39655273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pao W, Miller V, Zakowski M, Doherty J, Politi K, Sarkaria I, et al. . EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2004) 101(36):13306–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405220101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous