Unbalanced Redox With Autophagy in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 37265853
- PMCID: PMC10232220
- DOI: 10.12997/jla.2023.12.2.132
Unbalanced Redox With Autophagy in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
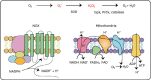
Precise redox balance is essential for the optimum health and physiological function of the human body. Furthermore, an unbalanced redox state is widely believed to be part of numerous diseases, ultimately resulting in death. In this review, we discuss the relationship between redox balance and cardiovascular disease (CVD). In various animal models, excessive oxidative stress has been associated with increased atherosclerotic plaque formation, which is linked to the inflammation status of several cell types. However, various antioxidants can defend against reactive oxidative stress, which is associated with an increased risk of CVD and mortality. The different cardiovascular effects of these antioxidants are presumably due to alterations in the multiple pathways that have been mechanistically linked to accelerated atherosclerotic plaque formation, macrophage activation, and endothelial dysfunction in animal models of CVD, as well as in in vitro cell culture systems. Autophagy is a regulated cell survival mechanism that removes dysfunctional or damaged cellular organelles and recycles the nutrients for the generation of energy. Furthermore, in response to atherogenic stress, such as the generation of reactive oxygen species, oxidized lipids, and inflammatory signaling between cells, autophagy protects against plaque formation. In this review, we characterize the broad spectrum of oxidative stress that influences CVD, summarize the role of autophagy in the content of redox balance-associated pathways in atherosclerosis, and discuss potential therapeutic approaches to target CVD by stimulating autophagy.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Autophagy; Cardiovascular disease; Inflammation; Oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2023 The Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Khosravi M, Poursaleh A, Ghasempour G, Farhad S, Najafi M. The effects of oxidative stress on the development of atherosclerosis. Biol Chem. 2019;400:711–732. - PubMed
-
- Seifried HE, Anderson DE, Fisher EI, Milner JA. A review of the interaction among dietary antioxidants and reactive oxygen species. J Nutr Biochem. 2007;18:567–579. - PubMed
-
- Sies H, Jones DP. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21:363–383. - PubMed
-
- Kamata H, Hirata H. Redox regulation of cellular signalling. Cell Signal. 1999;11:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

