Efficacy of ICI-based treatment in advanced NSCLC patients with PD-L1≥50% who developed EGFR-TKI resistance
- PMID: 37266427
- PMCID: PMC10230103
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1161718
Efficacy of ICI-based treatment in advanced NSCLC patients with PD-L1≥50% who developed EGFR-TKI resistance
Abstract
Introduction: Platinum-based chemotherapy is still the standard of care for Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients after developing EGFR-TKI resistance. However, no study focusing on the role of immuno checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) based treatments for EGFR mutated NSCLC patients who carried programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) tumor proportion score (TPS) greater than 50% progressed after EGFR-TKI therapy. In this study, we retrospectively investigated the outcomes of ICI-based treatments for EGFR mutated NSCLC patients carried PD-L1 TPS≥50% after developing EGFR-TKI resistance and to explore the population that may benefited from ICI-based treatment.
Methods: We retrospectively collected data of advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations and PD-L1 TPS≥50% who have failed prior EGFR-TKI therapies without T790M mutation at Shanghai Chest Hospital between January 2018 and June 2021. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were utilized to evaluate the outcomes of this study.
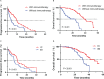
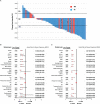
Results: A total of 146 patients were included. Up to June 20th, 2022, median follow-up was 36.7 months (IQR, 12.5-44.2 months). Among the population, 66 patients (45.2%) received chemotherapy, the remaning (54.8%) received ICI-based treatment, including 56 patients(70.0%) received ICI combined with chemotherapy (IC) and 24 patients (30.0%) received ICI monotherapy (IM). In IC group,31 patients received ICI combined with chemotherapy,19 patients received ICI combined with antiangiogenic therapy and remaing received ICI combined with chemotherapy and antiangiogenic therapy. Survival analysis shown that patients who received ICI-based treatment had better progress-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared with those treated with other therapy (median PFS, 10.0 vs. 4.0 months, P<0.001; median OS, 39.5 vs. 24.2 months, P<0.001). What's more, patients who treated with IC treatment had a superior survival time than those received IM treatment (median PFS, 10.3 vs. 7.0 months, P<0.001; median OS, 41.6 vs. 32.4 months, P<0.001). Subgroup analysis found that the PFS and OS benefit of IC was evident in all subgroups.
Conclusions: For advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations and PD-L1 TPS≥50% who have failed prior EGFR-TKI therapies without T790M mutation, ICI-based treatment could provide a more favorable survival than classical chemotherapy. What' s more, compared with ICI monotherapy, ICI combined with chemotherapy seems to be the preferred treatment.
Keywords: drug resistance; epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI); immunotherapy; non-small-cell lung cancer; programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1).
Copyright © 2023 Li, Jiang, Qian, Chen, Zhou, Zhang, Lu, Lou, Han and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

