Learning spatial frequency identification through reweighted decoding
- PMID: 37266934
- PMCID: PMC10243501
- DOI: 10.1167/jov.23.6.3
Learning spatial frequency identification through reweighted decoding
Abstract
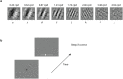
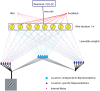
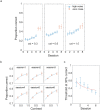
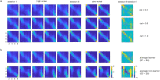
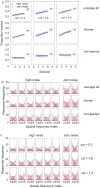
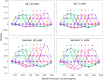
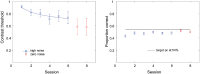
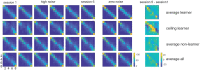
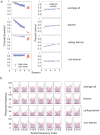
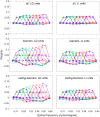
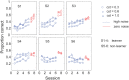
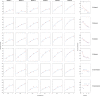
Perceptual learning, the improvement of perceptual judgments with practice, occurs in many visual tasks. There are, however, relatively fewer studies examining perceptual learning in spatial frequency judgments. In addition, perceptual learning has generally been studied in two-alternative tasks, occasionally in n-alternative tasks, and infrequently in identification. Recently, perceptual learning was found in an orientation identification task (eight-alternatives) and was well accounted for by a new identification integrated reweighting theory (I-IRT) (Liu et al., submitted). Here, we examined perceptual learning in a similar eight-alternative spatial frequency absolute identification task in two different training protocols, finding learning in the majority but not all observers. We fit the I-IRT to the spatial frequency learning data and discuss possible model explanations for variations in learning.
Figures
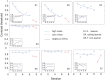
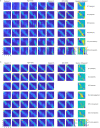
Similar articles
-
Transfer of visual perceptual learning over a task-irrelevant feature through feature-invariant representations: Behavioral experiments and model simulations.J Vis. 2024 Jun 3;24(6):17. doi: 10.1167/jov.24.6.17. J Vis. 2024. PMID: 38916886 Free PMC article.
-
Informational feedback accelerates learning in multi-alternative perceptual judgements of orientation.Vision Res. 2023 Dec;213:108318. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2023.108318. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Vision Res. 2023. PMID: 37742454
-
Perceptual learning for a pattern discrimination task.Vision Res. 2000;40(23):3209-30. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6989(00)00163-2. Vision Res. 2000. PMID: 11008139
-
Neural plasticity underlying visual perceptual learning in aging.Brain Res. 2015 Jul 1;1612:140-51. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.009. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25218557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visual Perceptual Learning and Models.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2017 Sep 15;3:343-363. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-102016-061249. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28723311 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transfer of visual perceptual learning over a task-irrelevant feature through feature-invariant representations: Behavioral experiments and model simulations.J Vis. 2024 Jun 3;24(6):17. doi: 10.1167/jov.24.6.17. J Vis. 2024. PMID: 38916886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahissar, M., & Hochstein, S. (1997). Task difficulty and the specificity of perceptual learning. Nature, 387(6631), 401–406. - PubMed
-
- Bakeman, R. (2005). Recommended effect size statistics for repeated measures designs. Behavior Research Methods, 37, 379–384. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, R. G., & Westheimer, G. (1991). The effect of training on visual alignment discrimination and grating resolution. Perception & Psychophysics, 49(6), 541–546. - PubMed
-
- Braida, L. D., Lim, J. S., Berliner, J. E., Durlach, N. I., Rabinowitz, W. M., & Purks, S. R. (1984). Intensity perception: XIII. Perceptual anchor model of context-coding. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 76, 722–731. - PubMed

