Pterostilbene mediates glial and immune responses to alleviate chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in nerve cells
- PMID: 37267263
- PMCID: PMC10237435
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286686
Pterostilbene mediates glial and immune responses to alleviate chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in nerve cells
Abstract
Chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) induces oxidative stress in the brain, causing sleep disorders. Herein, we investigated the role of pterostilbene (Pte) in CIH-mediated oxidative stress in the brain tissue. A CIH mouse model was constructed by alternately reducing and increasing oxygen concentration in a sealed box containing the mouse; brain tissue and serum were then collected after intragastric administration of Pte. Neurological function was evaluated through field experiments. The trajectory of the CIH mice to the central region initially decreased and then increased after Pte intervention. Pte increased the number of neuronal Nissl bodies in the hippocampus of CIH mice, upregulated the protein levels of Bcl-2, occludin, and ZO-1 as well as the mRNA and protein levels of cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB) and p-BDNF, and reduced the number of neuronal apoptotic cells, Bax protein levels, IBA-1, and GFAP levels. Simultaneously, Pte reversed the decreased levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), and BDNF and increased levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) in the serum of CIH mice. Pte increased Th2 cells, Treg cells, IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β1 levels and decreased Th1 cells, Th17 cells, IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL- 17A levels in activated BV2 cells and hippocampus in CIH mice. The protein levels of p-ERK1/2, TLR4, p-p38, p-p65, and Bax, apoptosis rate, MDA concentration, Bcl-2 protein level, cell viability, and SOD and GSH-PX concentrations decreased after the activation of BV2 cells. Pte inhibited gliocytes from activating T-cell immune imbalance through p-ERK signaling to alleviate oxidative stress injury in nerve cells.
Copyright: © 2023 Liu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

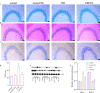
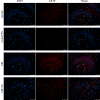
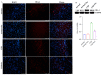
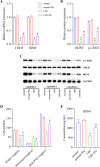
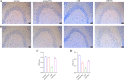
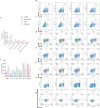
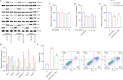
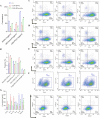
Similar articles
-
Melatonin attenuates hippocampal neuron apoptosis and oxidative stress during chronic intermittent hypoxia via up-regulating B-cell lymphoma-2 and down-regulating B-cell lymphoma-2-associated X protein.Saudi Med J. 2013 Jul;34(7):701-8. Saudi Med J. 2013. PMID: 23860889
-
Protocatechuic acid ameliorates neurocognitive functions impairment induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 30;5:14507. doi: 10.1038/srep14507. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26419512 Free PMC article.
-
[Hepatic injury in rats exposed to chronic intermittent hypoxia and the effect of tempol].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2012 Mar;35(3):189-92. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22781151 Chinese.
-
Influence of the TLR4-mediated p38MAPK signaling pathway on chronic intermittent hypoxic-induced rat's oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in rats.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jan;23(1):352-360. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201901_16783. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30657577
-
Neuroprotective effects of pterostilbene against oxidative stress injury: Involvement of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 pathway.Brain Res. 2016 Jul 15;1643:70-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.048. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27107941
Cited by
-
Brain nitric oxide and inflammation in chronic intermittent hypoxia: Contributors to cognitive impairment and hypertension.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Aug 4;48:101077. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.101077. eCollection 2025 Oct. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40808977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melittin Alleviates Oxidative Stress Injury in Schwann Cells by Targeting Interleukin-1 Receptor Type 1 to Downregulate Nuclear Factor Kappa B-Mediated Inflammatory Response In Vitro.Cureus. 2024 Jul 30;16(7):e65721. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65721. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39211643 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Neural Injury: Pathophysiology, Neurodegenerative Implications, and Therapeutic Insights.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Apr;31(4):e70384. doi: 10.1111/cns.70384. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40260643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cerebral Hypoxia-Induced Molecular Alterations and Their Impact on the Physiology of Neurons and Dendritic Spines: A Comprehensive Review.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug 6;44(1):58. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01491-4. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39105862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pterostilbene in the treatment of inflammatory and oncological diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1323377. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1323377. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38259272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Olaithe M, Bucks RS, Hillman DR, Eastwood PR. Cognitive deficits in obstructive sleep apnea: Insights from a meta-review and comparison with deficits observed in COPD, insomnia, and sleep deprivation. Sleep medicine reviews. 2018;38:39–49. Epub 2017/08/02. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2017.03.005 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

