Irisin acts through its integrin receptor in a two-step process involving extracellular Hsp90α
- PMID: 37267907
- PMCID: PMC10984146
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.05.008
Irisin acts through its integrin receptor in a two-step process involving extracellular Hsp90α
Abstract
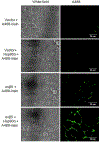
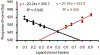
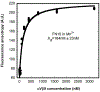
Exercise benefits the human body in many ways. Irisin is secreted by muscle, increased with exercise, and conveys physiological benefits, including improved cognition and resistance to neurodegeneration. Irisin acts via αV integrins; however, a mechanistic understanding of how small polypeptides like irisin can signal through integrins is poorly understood. Using mass spectrometry and cryo-EM, we demonstrate that the extracellular heat shock protein 90α (eHsp90α) is secreted by muscle with exercise and activates integrin αVβ5. This allows for high-affinity irisin binding and signaling through an Hsp90α/αV/β5 complex. By including hydrogen/deuterium exchange data, we generate and experimentally validate a 2.98 Å RMSD irisin/αVβ5 complex docking model. Irisin binds very tightly to an alternative interface on αVβ5 distinct from that used by known ligands. These data elucidate a non-canonical mechanism by which a small polypeptide hormone like irisin can function through an integrin receptor.
Keywords: HDX-MS; RGD motif; exercise; extracellular Hsp90; fibronectin III domain; integrin; integrin activation; irisin; ligand binding; protein-protein docking.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests B.M.S. holds several issued patents on irisin. B.M.S. is an academic co-founder of Aevum Therapeutics, which is attempting to develop irisin as a therapeutic. M.A. is a consultant to Aevum Therapeutics.
Figures






































Comment in
-
Extracellular HSP90 warms up integrins for an irisin workout.Cell Metab. 2023 Jul 11;35(7):1099-1100. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Cell Metab. 2023. PMID: 37327790 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

