LOX-1 mediates inflammatory activation of microglial cells through the p38-MAPK/NF-κB pathways under hypoxic-ischemic conditions
- PMID: 37268943
- PMCID: PMC10236821
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01048-w
LOX-1 mediates inflammatory activation of microglial cells through the p38-MAPK/NF-κB pathways under hypoxic-ischemic conditions
Abstract
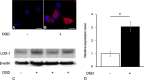
Background: Microglial cells play an important role in the immune system in the brain. Activated microglial cells are not only injurious but also neuroprotective. We confirmed marked lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) expression in microglial cells in pathological lesions in the neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (nHIE) model brain. LOX-1 is known to be an activator of cytokines and chemokines through intracellular pathways. Here, we investigated a novel role of LOX-1 and the molecular mechanism of LOX-1 gene transcription microglial cells under hypoxic and ischemic conditions.
Methods: We isolated primary rat microglial cells from 3-day-old rat brains and confirmed that the isolated cells showed more than 98% Iba-1 positivity with immunocytochemistry. We treated primary rat microglial cells with oxygen glucose deprivation (OGD) as an in vitro model of nHIE. Then, we evaluated the expression levels of LOX-1, cytokines and chemokines in cells treated with or without siRNA and inhibitors compared with those of cells that did not receive OGD-treatment. To confirm transcription factor binding to the OLR-1 gene promoter under the OGD conditions, we performed a luciferase reporter assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. In addition, we analyzed reactive oxygen species and cell viability.
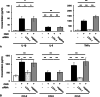
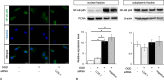
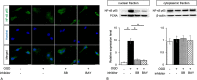
Results: We found that defects in oxygen and nutrition induced LOX-1 expression and led to the production of inflammatory mediators, such as the cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α; the chemokines CCL2, CCL5 and CCL3; and reactive oxygen/nitrogen species. Then, the LOX-1 signal transduction pathway was blocked by inhibitors, LOX-1 siRNA, the p38-MAPK inhibitor SB203580 and the NF-κB inhibitor BAY11-7082 suppressed the production of inflammatory mediators. We found that NF-κB and HIF-1α bind to the promoter region of the OLR-1 gene. Based on the results of the luciferase reporter assay, NF-κB has strong transcriptional activity. Moreover, we demonstrated that LOX-1 in microglial cells was autonomously overexpressed by positive feedback of the intracellular LOX-1 pathway.
Conclusion: The hypoxic/ischemic conditions of microglial cells induced LOX-1 expression and activated the immune system. LOX-1 and its related molecules or chemicals may be major therapeutic candidates. Video abstract.
Keywords: Hypoxia; Ischemia; LOX-1; Microglia; NF‐kappa B (NF‐κB); OLR-1; p38-MAPK.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to the contents of this article.
Figures


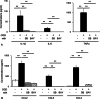
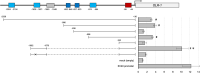
 , not significant compared with the SV40 promoter.
, not significant compared with the SV40 promoter.
 , TATA box;
, TATA box;
 , NF-κB binding site;
, NF-κB binding site;
 , OCT-1 binding site;
, OCT-1 binding site;
 , HIF-1α binding site;
, HIF-1α binding site;
 , mutation position
, mutation positionReferences
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

