pH-Responsive Hexa-Histidine Metal Assembly (HmA) with Enhanced Biocatalytic Cascades as the Vehicle for Glucose-Mediated Long-Acting Insulin Delivery
- PMID: 37269054
- PMCID: PMC10427356
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202301771
pH-Responsive Hexa-Histidine Metal Assembly (HmA) with Enhanced Biocatalytic Cascades as the Vehicle for Glucose-Mediated Long-Acting Insulin Delivery
Abstract
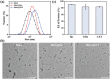
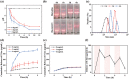
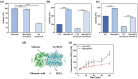
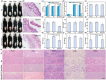
Diabetes has been listed as one of the three major diseases that endanger human health. Accurately injecting insulin (Ins) depending on the level of blood glucose (LBG) is the standard treatment, especially controlling LBG in the long-term by a single injection. Herein, the pH-responsive hexa-histidine metal assembly (HmA) encapsulated with enzymes (GOx and CAT) and Ins (HmA@GCI) is engineered as the vehicle for glucose-mediated insulin delivery. HmA not only shows high proteins loading efficiency, but also well retained proteins activity and protect proteins from protease damage. Within HmA, the biocatalytic activities of enzymes and the efficiency of the cascade reaction between GOx and CAT are enhanced, leading to a super response to the change of LBG with insulin release and efficient clearance of harmful byproducts of GOx (H2 O2 ). In the treatment of diabetic mice, HmA@GCI reduces LBG to normal in half an hour and maintains for more than 5 days by a single subcutaneous injection, and nearly 24 days with four consecutive injections. During the test period, no symptoms of hypoglycemia and toxicity to tissues and organs are observed. These results indicate that HmA@GCI is a safe and long-acting hypoglycemic agent with prospective clinical application.
Keywords: diabetes; glucose-response; hexahistidine-metal-assembly; insulin delivery; pH sensitive.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Erythrocyte-Membrane-Enveloped Biomineralized Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles Enable Intravenous Glucose-Responsive Insulin Delivery.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 May 5;13(17):19648-19659. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c01943. Epub 2021 Apr 23. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33890785
-
[Application of hyaluronic acid microneedles in insulin intelligent delivery system for the treatment of diabetes].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022 Sep 25;38(9):3433-3442. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.220129. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 36151811 Chinese.
-
Ultrafast glucose-responsive, high loading capacity erythrocyte to self-regulate the release of insulin.Acta Biomater. 2018 Mar 15;69:301-312. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.01.029. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29421303
-
Insulin during pregnancy, labour and delivery.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011 Feb;25(1):65-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011. PMID: 21186142 Review.
-
Optimizing the replacement of basal insulin in type 1 diabetes mellitus: no longer an elusive goal in the post-NPH era.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011 Jun;13 Suppl 1:S43-52. doi: 10.1089/dia.2011.0039. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21668336 Review.
Cited by
-
Procyanidin capsules provide a new option for long-term ROS scavenging in chronic inflammatory diseases.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Oct 24;29:101310. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101310. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39534678 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Hard Shell with Soft Core to Enhance Enzyme Activity and Resist External Disturbances.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(10):e2411196. doi: 10.1002/advs.202411196. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39840556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tripathi B. K., Srivastava A. K., Med. Sci. Monit. 2006, 12, RA130. - PubMed
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B. B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J. C. N., Mbanya J. C., Pavkov M. E., Ramachandaran A., Wild S. H., James S., Herman W. H. H., Zhang P., Bommer C., Kuo S. H., Boyko E. J. J., Magliano D. J., Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kramer C. K., Retnakaran R., Zinman B., Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 740. - PubMed
-
- Ravaine V., Ancla C., Catargi B., J. Controlled Release 2008, 132, 2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
