Iodine loaded nanoparticles with commercial applicability increase survival in mice cancer models with low degree of side effects
- PMID: 37269144
- PMCID: PMC10432436
- DOI: 10.1002/cnr2.1843
Iodine loaded nanoparticles with commercial applicability increase survival in mice cancer models with low degree of side effects
Abstract
Background: The recorded use of iodine in medicine, dates to 5000 BC. Molecular iodine (I2 ) has been claimed to exert an antineoplastic effect that triggers apoptotic and re-differentiation mechanisms in different types of cancer cells in animal studies. Hitherto, all experiments published have been carried out with I2 diluted in water preparations resulting in the administration of ionized iodide, either alone or in combination with low levels of I2 . To maximize the levels of I2 by avoiding water solutions we have managed to develop a colloidal nano particle (NP) loaded with I2 with a Z-average of 7-23 nm with remarkable stability, preferable osmolality and commercial applicability.
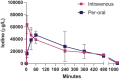
Aims: Here we report the results from formulation and pre-clinical studies with the rationale: a) to find a tolerable dose of the I2 NP system delivered intravenously or per-orally, and b) to determine if the tolerable doses are efficacious in murine models of cancer.
Methods and results: A novel drug delivery system with I2 NP was formulated and murine cancer models with CT26, MDA-MB-231 and LL/2 cells were used to analyse the efficacy. Despite the formulation challenges we were successful in constructing stable NPs loaded with I2 which have convincing commercial applicability. We conclude that administration of the NP I2 drug delivery system: 1. Blunted tumour growth in a xenograft breast cancer model; 2. Had a significant effect on survival in the orthotopic, syngeneic lung metastasis model; 3. Showed reduced tumour burden in post-mortem evaluation and; 4. Was associated with low degree of side effects.
Conclusions: Taken all together, our findings indicate that the NP I2 drug delivery system may serve as a novel effective cancer treatment with low degree of side effects. This is something which needs further exploration including confirmation in future clinical trials.
Keywords: cytotoxic; drug delivery; molecular iodine; nanoparticles; side effects.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Colloidal Iodine is being developed by Shigeru AG which financed the research and development performed by Adlego/Scantox and APL without any demands of retribution
Figures





Similar articles
-
The in vivo fate of nanoparticles and nanoparticle-loaded microcapsules after oral administration in mice: Evaluation of their potential for colon-specific delivery.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Aug;94:393-403. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.06.014. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 26117186
-
Therapeutic efficacy and molecular mechanisms of snake (Walterinnesia aegyptia) venom-loaded silica nanoparticles in the treatment of breast cancer- and prostate cancer-bearing experimental mouse models.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:175-189. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.018. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23811005
-
Poly(lactide)-vitamin E derivative/montmorillonite nanoparticle formulations for the oral delivery of Docetaxel.Biomaterials. 2009 Jul;30(19):3297-306. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.02.045. Epub 2009 Mar 19. Biomaterials. 2009. PMID: 19299012
-
Nanoparticles in drug delivery: mechanism of action, formulation and clinical application towards reduction in drug-associated nephrotoxicity.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014 Oct;11(10):1661-80. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.938046. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 25054316 Review.
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

