EETs alleviate alveolar epithelial cell senescence by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress through the Trim25/Keap1/Nrf2 axis
- PMID: 37269686
- PMCID: PMC10249012
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102765
EETs alleviate alveolar epithelial cell senescence by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress through the Trim25/Keap1/Nrf2 axis
Abstract
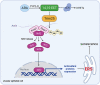
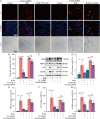
Alveolar epithelial cell (AEC) senescence is a key driver of a variety of chronic lung diseases. It remains a challenge how to alleviate AEC senescence and mitigate disease progression. Our study identified a critical role of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), downstream metabolites of arachidonic acid (ARA) by cytochrome p450 (CYP), in alleviating AEC senescence. In vitro, we found that 14,15-EET content was significantly decreased in senescent AECs. Exogenous EETs supplementation, overexpression of CYP2J2, or inhibition of EETs degrading enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) to increase EETs alleviated AECs' senescence. Mechanistically, 14,15-EET promoted the expression of Trim25 to ubiquitinate and degrade Keap1 and promoted Nrf2 to enter the nucleus to exert an anti-oxidant effect, thereby inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and alleviating AEC senescence. Furthermore, in D-galactose (D-gal)-induced premature aging mouse model, inhibiting the degradation of EETs by Trifluoromethoxyphenyl propionylpiperidin urea (TPPU, an inhibitor of sEH) significantly inhibited the protein expression of p16, p21, and γH2AX. Meanwhile, TPPU reduced the degree of age-related pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Our study has confirmed that EETs are novel anti-senescence substances for AECs, providing new targets for the treatment of chronic lung diseases.
Keywords: Alveolar epithelial cells; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; Senescence; Tripartite motif-containing 25.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids alleviate alveolar epithelial cell senescence by inhibiting mitophagy through NOX4/Nrf2 pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Dec 31;169:115937. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115937. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 38007934
-
COX-2/sEH dual inhibitor PTUPB alleviates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via inhibiting senescence.FEBS J. 2020 Apr;287(8):1666-1680. doi: 10.1111/febs.15105. Epub 2019 Nov 8. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 31646730 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Pharmacological Inhibition Decreases Alveolar Bone Loss by Modulating Host Inflammatory Response, RANK-Related Signaling, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Apoptosis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017 Jun;361(3):408-416. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.238113. Epub 2017 Mar 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017. PMID: 28356494 Free PMC article.
-
Role of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in cardiovascular diseases and cardiotoxicity of drugs.Life Sci. 2022 Dec 1;310:121122. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121122. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36309225 Review.
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids and Fibrosis: Recent Insights for the Novel Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 3;22(19):10714. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910714. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morusin Alleviates Aortic Valve Calcification by Inhibiting Valve Interstitial Cell Senescence Through Ccnd1/Trim25/Nrf2 Axis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 May;11(20):e2307319. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307319. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38502885 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular senescence of granulosa cells in the pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome.Mol Hum Reprod. 2024 Apr 30;30(5):gaae015. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaae015. Mol Hum Reprod. 2024. PMID: 38603629 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt5a-mediated autophagy contributes to the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human bronchial epithelial cells during asthma.Mol Med. 2024 Jun 19;30(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00862-3. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38898476 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting alveolar epithelial cell metabolism in pulmonary fibrosis: Pioneering an emerging therapeutic strategy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 25;13:1608750. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1608750. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40636669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adhesive and injectable hydrogel microspheres for NRF2-mediated periodontal bone regeneration.Int J Oral Sci. 2025 Jan 10;17(1):7. doi: 10.1038/s41368-024-00340-w. Int J Oral Sci. 2025. PMID: 39788942 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

