Fabrication and optimization of itraconazole-loaded zein-based nanoparticles in coated capsules as a promising colon-targeting approach pursuing opportunistic fungal infections
- PMID: 37270444
- PMCID: PMC10624751
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-023-01365-0
Fabrication and optimization of itraconazole-loaded zein-based nanoparticles in coated capsules as a promising colon-targeting approach pursuing opportunistic fungal infections
Abstract
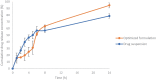
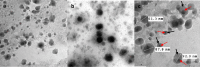
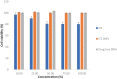
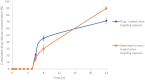
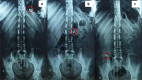
Itraconazole (ITZ), a broad-spectrum antifungal drug, was formulated into colon-targeting system aiming to treat opportunistic colonic fungal infections that commonly infect chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) patients due to immunosuppressive therapy. Antisolvent precipitation technique was employed to formulate ITZ-loaded zein nanoparticles (ITZ-ZNPs) using various zein: drug and aqueous:organic phase ratios. Central composite face-centered design (CCFD) was used for statistical analysis and optimization. The optimized formulation was composed of 5.5:1 zein:drug ratio and 9.5:1 aqueous:organic phase ratio with its observed particle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, and entrapment efficiency of 208 ± 4.29 nm, 0.35 ± 0.04, 35.7 ± 1.65 mV, and 66.78 ± 3.89%, respectively. ITZ-ZNPs were imaged by TEM that revealed spherical core-shell structure, and DSC proved ITZ transformation from crystalline to amorphous form. FT-IR showed coupling of zein NH group with ITZ carbonyl group without affecting ITZ antifungal activity as confirmed by antifungal activity test that showed enhanced activity of ITZ-ZNPs over the pure drug. Histopathological examination and cytotoxicity tests ensured biosafety and tolerance of ITZ-ZNPs to the colon tissue. The optimized formulation was then loaded into Eudragit S100-coated capsules and both in vitro release and in vivo X-ray imaging confirmed the success of such coated capsules in protecting ITZ from the release in stomach and intestine while targeting ITZ to the colon. The study proved that ITZ-ZNPs is promising and safe nanoparticulate system that can protect ITZ throughout the GIT and targeting its release to the colon with effectual focused local action for the treatment of colon fungal infections.
Keywords: Central composite face-centered design (CCFD); Colon fungal infections; Colon targeting; Itraconazole; Zein nanoparticles.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

