Dexmedetomidine versus haloperidol for sedation of non-intubated patients with hyperactive delirium during the night in a high dependency unit: study protocol for an open-label, parallel-group, randomized controlled trial (DEX-HD trial)
- PMID: 37270483
- PMCID: PMC10239100
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02158-1
Dexmedetomidine versus haloperidol for sedation of non-intubated patients with hyperactive delirium during the night in a high dependency unit: study protocol for an open-label, parallel-group, randomized controlled trial (DEX-HD trial)
Abstract
Background: Delirium is common in critically ill patients. Haloperidol has long been used for the treatment of delirium. Dexmedetomidine has recently been used to treat delirium among intubated critically ill patients. However, the efficacy of dexmedetomidine for delirium in non-intubated critically ill patients remains unknown. We hypothesize that dexmedetomidine is superior to haloperidol for sedation of patients with hyperactive delirium, and would reduce the prevalence of delirium among non-intubated patients after administration. We will conduct a randomized controlled trial to compare dexmedetomidine and haloperidol for the treatment of nocturnal hyperactive delirium in non-intubated patients in high dependency units (HDUs).
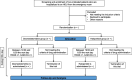
Methods: This is an open-label, parallel-group, randomized controlled trial to compare the efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine and haloperidol for nocturnal hyperactive delirium in non-intubated patients at two HDUs of a tertiary hospital. We will recruit consecutive non-intubated patients who are admitted to the HDU from the emergency room, and allocate them in a 1:1 ratio to the dexmedetomidine or haloperidol group in advance. The allocated investigational drug will be administered only when participants develop hyperactive delirium (Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale [RASS] score ≥1 and a positive score on the Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU between 19:00 and 6:00 the next day) during the night at an HDU. Dexmedetomidine is administered continuously, while haloperidol is administered intermittently. The primary outcome is the proportion of participants who achieve the targeted sedation level (RASS score of between -3 and 0) 2h after the administration of the investigational drug. Secondary outcomes include the sedation level and prevalence of delirium on the day following the administration of the investigational drugs, and safety. We plan to enroll 100 participants who develop nocturnal hyperactive delirium and receive one of the two investigational drugs.
Discussion: This is the first randomized controlled trial to compare the efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine and haloperidol for sedation of non-intubated critically ill patients with hyperactive delirium in HDUs. The results of this study may confirm whether dexmedetomidine could be another option to sedate patients with hyperactive delirium.
Trial registration: Japan Registry of Clinical Trials, jRCT1051220015, registered on 21 April 2022.
Keywords: Agitation; Delirium; Dexmedetomidine; Haloperidol; Hospital units; Intubation; Pharmacotherapy; Randomized controlled trial; Sedatives.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ely EW, Girard TD, Shintani AK, Jackson JC, Gordon SM, Thomason JWW, et al. Apolipoprotein E4 polymorphism as a genetic predisposition to delirium in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:112–7. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000251925.18961.CA. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous