Storming the gate: New approaches for targeting the dynamic tight junction for improved drug delivery
- PMID: 37271282
- PMCID: PMC10999255
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.114905
Storming the gate: New approaches for targeting the dynamic tight junction for improved drug delivery
Abstract
As biologics used in the clinic outpace the number of new small molecule drugs, an important challenge for their efficacy and widespread use has emerged, namely tissue penetrance. Macromolecular drugs - bulky, high-molecular weight, hydrophilic agents - exhibit low permeability across biological barriers. Epithelial and endothelial layers, for example within the gastrointestinal tract or at the blood-brain barrier, present the most significant obstacle to drug transport. Within epithelium, two subcellular structures are responsible for limiting absorption: cell membranes and intercellular tight junctions. Previously considered impenetrable to macromolecular drugs, tight junctions control paracellular flux and dictate drug transport between cells. Recent work, however, has shown tight junctions to be dynamic, anisotropic structures that can be targeted for delivery. This review aims to summarize new approaches for targeting tight junctions, both directly and indirectly, and to highlight how manipulation of tight junction interactions may help usher in a new era of precision drug delivery.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


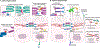
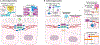
Similar articles
-
Potential use of tight junction modulators to reversibly open membranous barriers and improve drug delivery.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Apr;1788(4):892-910. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.09.016. Epub 2008 Oct 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18983815 Review.
-
Paracellular drug absorption enhancement through tight junction modulation.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2013 Jan;10(1):103-14. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2013.745509. Epub 2012 Nov 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2013. PMID: 23163247 Review.
-
Reversible Opening of Intercellular Junctions of Intestinal Epithelial and Brain Endothelial Cells With Tight Junction Modulator Peptides.J Pharm Sci. 2016 Feb;105(2):754-765. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2015.11.018. J Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 26869428
-
Modulation of tight junctions does not predict oral absorption of hydrophilic compounds: use of Caco-2 and Calu-3 cells.Arch Pharm Res. 2007 Aug;30(8):1002-7. doi: 10.1007/BF02993969. Arch Pharm Res. 2007. PMID: 17879754
-
[Claudins as tight junction proteins: the molecular element of paracellular transport].Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2013 Feb;99(2):175-95. Ross Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 2013. PMID: 23650732 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology to Overcome Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 20;17(3):281. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030281. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40142945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced Anti-Melanoma Activity of Nutlin-3a Delivered via Ethosomes: Targeting p53-Mediated Apoptosis in HT144 Cells.Cells. 2024 Oct 11;13(20):1678. doi: 10.3390/cells13201678. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39451196 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Encapsulation of Multiple Antineoplastic Agents in Liposomes by Exploring Microfluidics.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 17;26(8):3820. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083820. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Drug Blood-Brain-Barrier Permeability Using a Microfluidic Chip.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Apr 23;16(5):574. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050574. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794236 Free PMC article.
-
Paracellular Delivery of Protein Drugs with Smart EnteroPatho Nanoparticles.ACS Nano. 2024 Aug 13;18(32):21038-21051. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c02116. Epub 2024 Aug 3. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39096293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown TD, Whitehead KA, Mitragotri S, Materials for oral delivery of proteins and peptides, Nat. Rev. Mater 5 (2020) 127–148, 10.1038/s41578-019-0156-6. - DOI
-
- Zhu L, Lu L, Wang S, Wu J, Shi J, Yan T, Xie C, Li Q, Hu M, Liu Z, Chapter 11 - Oral Absorption Basics: Pathways and Physicochemical and Biological Factors Affecting Absorption, in: Qiu Y, Chen Y, Zhang GGZ, Yu L, Mantri RV (Eds.), Dev. Solid Oral Dos. Forms, Second Ed., Academic Press, Boston, 2017, pp. 297–329, 10.1016/B978-0-12-802447-8.00011-X. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

