Demodex Blepharitis: A Comprehensive Review of the Disease, Current Management, and Emerging Therapies
- PMID: 37272680
- PMCID: PMC10351901
- DOI: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000001003
Demodex Blepharitis: A Comprehensive Review of the Disease, Current Management, and Emerging Therapies
Abstract
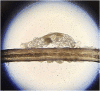
Demodex blepharitis is a common disease of the eyelid, affecting approximately 25 million Americans. This article reviews what is known about the mechanisms and impact of Demodex blepharitis, risk factors, signs and symptoms, diagnostic techniques, current management options, and emerging treatments. Demodex mites contribute to blepharitis in several ways: direct mechanical damage, as a vector for bacteria, and by inducing hypersensitivity and inflammation. Risk factors for Demodex blepharitis include increasing age, rosacea, and diabetes. The costs, symptom burden, and psychosocial effects of Demodex blepharitis are considerable. The presence of collarettes is pathognomonic for Demodex blepharitis. Redness, dryness, discomfort, foreign body sensation, lash anomalies, and itching are also hallmarks of the disease. Although a number of oral, topical, eyelid hygiene and device-based options have been used clinically and evaluated in studies for the management of Demodex blepharitis, none have been FDA approved to treat the disease. Recent randomized controlled clinical trials suggest that lotilaner ophthalmic solution, 0.25%, is a topical treatment with the potential to eradicate Demodex mites and eliminate collarettes and eyelid redness for an extended period.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the CLAO.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Barnett, D. K. Dhaliwal, I. B. Gaddie, P. Karpecki, K. K. Nichols, C. J. Rapuano, and E. Yeu are consultants for Tarsus Pharmaceuticals. P. Karpecki is also a consultant for Azura, BioTissue, Bruder, Oasis Medical, OCuSOFT, Scope, and Thea. K. K. Nichols is also a consultant for Bruder and Thea. A. Chan, P. Karpecki, J. Mun, and E. Yeu have equity interests in Tarsus Pharmaceuticals. A. Chan and J. Mun are employees of Tarsus Pharmaceuticals. F. S. Mah and M. K. Rhee report no conflicts of interest related to the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Amescua G, Akpek EK, Farid M, et al. . Blepharitis preferred practice Pattern®. Ophthalmology 2019;126:PP56-93. - PubMed
-
- Zhang AC, Muntz A, Wang MTM, et al. Ocular demodex: A systematic review of the clinical literature. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2020;40:389–432. - PubMed
-
- Shah PP, Stein RL, Perry HD. Update on the management of demodex blepharitis. Cornea 2022;41:934–939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

