Genome-wide Association Study for AKI
- PMID: 37273234
- PMCID: PMC10371295
- DOI: 10.34067/KID.0000000000000175
Genome-wide Association Study for AKI
Abstract
Key Points:
Two genetic variants in the DISP1-TLR5 gene locus were associated with risk of AKI.
DISP1 and TLR5 were differentially regulated in kidney biopsy tissue from patients with AKI compared with no AKI.
Background: Although common genetic risks for CKD are well established, genetic factors influencing risk for AKI in hospitalized patients are poorly understood.
Methods: We conducted a genome-wide association study in 1369 participants in the Assessment, Serial Evaluation, and Subsequent Sequelae of AKI Study; a multiethnic population of hospitalized participants with and without AKI matched on demographics, comorbidities, and kidney function before hospitalization. We then completed functional annotation of top-performing variants for AKI using single-cell RNA sequencing data from kidney biopsies in 12 patients with AKI and 18 healthy living donors from the Kidney Precision Medicine Project.
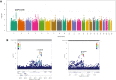
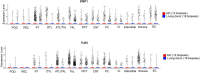
Results: No genome-wide significant associations with AKI risk were found in Assessment, Serial Evaluation, and Subsequent Sequelae of AKI (P < 5×10−8). The top two variants with the strongest association with AKI mapped to the dispatched resistance-nodulation-division (RND) transporter family member 1 (DISP1) gene and toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) gene locus, rs17538288 (odds ratio, 1.55; 95% confidence interval, 1.32 to 182; P = 9.47×10−8) and rs7546189 (odds ratio, 1.53; 95% confidence interval, 1.30 to 1.81; P = 4.60×10−7). In comparison with kidney tissue from healthy living donors, kidney biopsies in patients with AKI showed differential DISP1 expression in proximal tubular epithelial cells (adjusted P = 3.9×10−2) and thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle (adjusted P = 8.7×10−3) and differential TLR5 gene expression in thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle (adjusted P = 4.9×10−30).
Conclusions: AKI is a heterogeneous clinical syndrome with various underlying risk factors, etiologies, and pathophysiology that may limit the identification of genetic variants. Although no variants reached genome-wide significance, we report two variants in the intergenic region between DISP1 and TLR5, suggesting this region as a novel risk for AKI susceptibility.
Conflict of interest statement
P.K. Bhatraju reports the following: Research Funding: Roche Diagnostics. V.M. Chinchilli reports the following: Advisory or Leadership Role: Allergan; Astra-Zeneca; Biohaven; Jannsen; Regeneron; Sanofi. S.G. Coca reports the following: Consultancy: 3ive, Axon, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Nuwellis, Renalytix, Reprieve Cardiovascular, Takeda, Vifor; Ownership Interest: pulseData, Renalytix; Research Funding: ProKidney, Renal Research Institute, Renalytix, XORTX; Patents or Royalties: Renalytix; and Other Interests or Relationships: Associate Editor for
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UH3 DK114923/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK133177/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114920/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U2C DK114886/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114908/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK099923/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114915/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114907/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114866/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK105124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098233/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK116967/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK125529/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK133090/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082223/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK084012/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101507/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK088964/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082192/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114870/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 DK114861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK120811/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL085757/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK113381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114926/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 TR002158/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 DK114926/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008680/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK128538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HS027626/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- U01 DK106962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UH3 DK114937/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

