GL67 lipid-based liposomal formulation for efficient siRNA delivery into human lung cancer cells
- PMID: 37273265
- PMCID: PMC10236467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.05.017
GL67 lipid-based liposomal formulation for efficient siRNA delivery into human lung cancer cells
Abstract
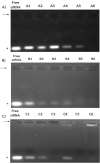
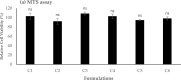
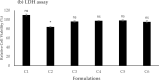
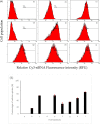
The efficient delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) to the targeted cells significantly affects the regulation of the overexpressed proteins involved in the progression of several genetic diseases. SiRNA molecules in naked form suffer from low internalization across the cell membrane, high susceptibility to degradation by nuclease enzyme and low stability, which hinder their efficacy. Therefore, there is an urge to develop a delivery system that can protect siRNA from degradation and facilitate their uptake across the cell membrane. In this study, the cationic lipid (GL67) was exploited, in addition to DC-Chol and DOPE lipids, to design an efficient liposomal nanocarrier for siRNA delivery. The physiochemical characterizations demonstrated that the molar ratio of 3:1 has proper particle size measurements from 144 nm to 332 nm and zeta potential of -9 mV to 47 mV that depends on the ratio of the GL67 in the liposomal formulation. Gel retardation assay exhibited that increasing the percentage of GL67 in the formulations has a good impact on the encapsulation efficiency compared to DC-Chol. The optimal formulations of the 3:1 M ratio also showed high metabolic activity against A549 cells following a 24 h cell exposure. Flow cytometry findings showed that the highest GL67 lipid ratio (100 % GL67 and 0 % DC-Chol) had the highest percentage of cellular uptake. The lipoplex nanocarriers based on GL67 lipid could potentially influence treating genetic diseases owing to the high internalization efficiency and safety profile.
Keywords: A549 cells; GL67 lipid; Gene therapy; Liposomes; siRNA delivery.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative silencing of EGFP reporter gene by self-assembled siRNA lipoplexes of LinOS and cholesterol.Mol Pharm. 2012 Nov 5;9(11):3384-95. doi: 10.1021/mp300435x. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Mol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 23057412 Free PMC article.
-
DC-Chol/DOPE cationic liposomes: a comparative study of the influence factors on plasmid pDNA and siRNA gene delivery.Int J Pharm. 2010 May 10;390(2):198-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.01.035. Epub 2010 Jan 29. Int J Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20116418
-
Lipidic carriers of siRNA: differences in the formulation, cellular uptake, and delivery with plasmid DNA.Biochemistry. 2004 Oct 26;43(42):13348-56. doi: 10.1021/bi048950a. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15491141
-
Liposomal siRNA nanocarriers for cancer therapy.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014 Feb;66:110-6. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.12.008. Epub 2013 Dec 30. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014. PMID: 24384374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative lipoplexes formulations with enhanced siRNA efficacy for cancer treatment: Where are we now?Int J Pharm. 2021 Aug 10;605:120851. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120851. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34217823 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advancement in mRNA Vaccine Development and Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 18;15(7):1972. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071972. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of nucleic acids using nanomaterials.Mol Biomed. 2023 Dec 14;4(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00160-0. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 38092998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication and evaluation of ribavirin-loaded electrospun nanofibers as an antimicrobial wound dressing.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 May;32(5):102058. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102058. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38601973 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-mediated dsRNA delivery for precision insect pest control: a comprehensive review.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 24;51(1):355. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09187-6. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38400844 Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review of mRNA-based Vaccines for COVID-19, A New Era in Pharmaceuticals: Unspecified and Unknown Aspects, Effects and Challenges.Curr Top Med Chem. 2025;25(12):1467-1491. doi: 10.2174/0115680266325847241121034100. Curr Top Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39779563 Review.
References
-
- A549 | ATCC, Available at: https://www.atcc.org/products/ccl-185. Accessed April 04, 2023.
-
- Alkahtani M.H., Almuqhim A.A., Alshehri A.A., et al. Fluorescent ruby nanocrystals for biocompatible applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021;118 doi: 10.1063/5.0054775. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

