Dealing with infodemic during COVID-19 pandemic: Role of effective health communication in facilitating outbreak response & actions - An ICMR experience
- PMID: 37274124
- PMCID: PMC10219680
- DOI: 10.1016/j.puhip.2023.100394
Dealing with infodemic during COVID-19 pandemic: Role of effective health communication in facilitating outbreak response & actions - An ICMR experience
Abstract
Objectives: To highlight and assess the impact of intervention tools used by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) against COVID19 associated infodemic in the world's largest democratic country, India.
Study design: It is a retrospective cross sectional study. The impact of ICMR's multi-pronged strategy to address the infodemic during pandemic has been assessed through analysis of print media reportage and social media engagements.
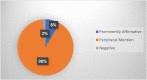
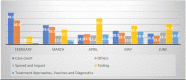
Methods: The impact of the interventions was assessed using cloud media mappers like MediaCloud and Meltwater using keywords. The data was analysed in terms of reportage, theme of reportage. A sub-section of media reportage (Feb 2020-June 2020) was analysed in details from 4 major dailies to understand the coverage and tonality of media reports. The data on COVID 19 related tweets, posts and uploads were taken from social media platforms of Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) particularly twitter, instagram, facebook and youtube and estimate of pre and post pandemic changes in followers or users were collected for analysis. The data was curated and analysed using MS excel.
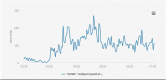
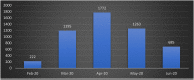
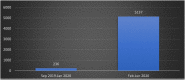
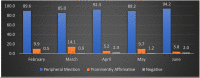
Results: There was a surge of 3800% reportage in media during pandemic as compared to same time frame in pre-pandemic times. A surge of followers on twitter from 26,823 on Feb 2020 (before pandemic) to 3,36,098 at March 2022 (after pandemic) was observed. A drastic increase in monthly followers was observed after start of Pandemic (after Feb 2020) in comparison to before pandemic (Before Feb 2020). Similar trends were observed on other social media platforms of ICMR.
Conclusions: The Communications Unit at ICMR geared up with more robust plans and designed several interventions to mitigate the infodemic which helped in evidence based decision making towards outbreak response and action. This highlights the importance of evidence based, crisp, timely and effective communication during the epidemics/pandemics to buid trust and confidence in the community.
Keywords: COVID19; Communications; Infodemic; Media; Pandemic.
© 2023 Indian Council of Medical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization Managing the COVID-19 infodemic: promoting healthy behaviors and mitigating the harm from misinformation and disinformation. Sept 2020. https://www.who.int/news/item/23-09-2020-managing-the-covid-19-infodemic... Available at: :
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

