Systematic evaluation of combined herbal adjuvant therapy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 37274344
- PMCID: PMC10232951
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1157189
Systematic evaluation of combined herbal adjuvant therapy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of combined traditional Chinese medicine in the adjuvant treatment of proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) by Meta-analysis.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang databases were searched by computer. Random controlled clinical trials (RCTS) using traditional Chinese medicine as adjuvant therapy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy were screened, and Stata16.0 software was used to perform meta-analysis on the final included literatures.
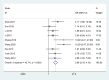
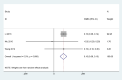
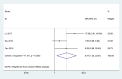
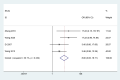
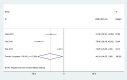
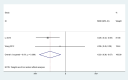
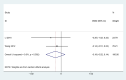
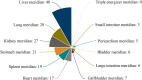
Results: A total of 18 studies involving 1392 patients were included. Meta-analysis showed that the clinical effective rate OR=2.99 (CI: 2.18-4.10, I2 = 42.7%, P<0.05); Visual acuity MD=0.10(CI: 0.06-0.13, I2 = 0%, P<0.05); Fundus efficacy OR=5.47 (CI: 1.33-22.51, I2 = 71.4%, P<0.05); Neovascularisation regression rate OR=8 (CI: 3.83-16.71, I2 = 30.1%, P<0.05); Macular foveal thickness MD=-44.24 (CI: -84.55-3.93, I2 = 95.6%, P<0.05); Absorption of vitreous hemorrhage OR=4.7 (CI: 2.26-9.77, I2 = 0%, P<0.05); Fasting blood glucose MD=-0.23, (CI: -0.38-0.07, I2 = 0%, P<0.05); 2h postprandial blood glucose MD=-0.19 (CI: -0.52-0.14, I2 = 0%, P=0.25). From the results, the combined Chinese medicine adjuvant therapy showed better efficacy than the control group. A total of 69 kinds of traditional Chinese medicine were involved in 18 studies, among which the top four applied frequencies were Panax notoginseng, Rehmannia rehmannii, Astragalus membranaceus and Poria cocos. Most of the medicines were sweet and bitter in taste, the qi tended to be slight cold and cold, and the meridian tropism belongs to the liver meridian.
Conclusion: The combination of traditional Chinese medicine adjuvant therapy has a good curative effect on PDR patients. However, the relevant clinical trials are few and more high-quality clinical trials are still needed, what's more the attention should be paid to the exploration of its safety.
Keywords: Chinese medicinal herb; diabetic complications; meta analysis; proliferative diabetic retinopathy; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Huai, Huai, Su, Song, Li, Cao, Xin and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Single herbal medicine for diabetic retinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 19;12(12):CD007939. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007939.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30566763 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Chinese herbal compounds on ocular fundus signs and vision in conventional treated-persons with non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 11;13:977971. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.977971. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36034416 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Chinese Patent Medicines on Ocular Fundus Signs and Vision in Calcium Dobesilate-Treated Persons With Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 14;13:799337. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.799337. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35370950 Free PMC article.
-
Panax notoginseng preparations as adjuvant therapy for diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):138-145. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1711782. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 31967924 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional chinese medicine for diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Feb;99(7):e19102. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019102. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32049817 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dilemmas in Elderly Diabetes and Clinical Practice Involving Traditional Chinese Medicine.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;17(7):953. doi: 10.3390/ph17070953. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of traditional Chinese medicine in age-related macular degeneration: exploring the gut microbiota's influence.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 25;15:1356324. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1356324. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38333011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An evidence mapping study based on systematic reviews of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for diabetic retinopathy.Syst Rev. 2025 Feb 20;14(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13643-025-02755-w. Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39980075 Free PMC article.
-
GPR30-driven fatty acid oxidation targeted by ginsenoside Rd maintains mitochondrial redox homeostasis to restore vascular barrier in diabetic retinopathy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Mar 14;24(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02638-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40087616 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Training Content Index System for Pressure Injury Prevention Training Programs for Healthcare Assistants in Tertiary Hospitals.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025 Jun 18;18:2021-2034. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S516689. eCollection 2025. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2025. PMID: 40546454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Group NATG. Technical scheme of grading diagnosis and treatment service for diabetic retinopathy. Chin J Gen Practitioners (2017) 16:589–93. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2017.08.005 - DOI
-
- Chen Q, Ni Q, Liu Y. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of diabetic retinopathy ( 2021-09-24 ). World Tradition Chin Med (2021) 16:3270–77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2021.22.002 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

