Trends of Prevalence Estimates and Risk Factors of Depressive Symptoms among Healthcare Workers Over one Year of the COVID-19 Pandemic
- PMID: 37274865
- PMCID: PMC10158079
- DOI: 10.2174/17450179-v18-e2206160
Trends of Prevalence Estimates and Risk Factors of Depressive Symptoms among Healthcare Workers Over one Year of the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 pandemic has an overwhelming psychologic burden on healthcare workers (HCWs). This study aims to investigate the changes in the prevalence, estimates, severity, and risk factors of depressive symptoms among HCWs within the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: An observational e-survey collected data on HCWs' socio-demographic characteristics, occupational situation, and depressive symptoms as measured by Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). The e-survey was distributed one month after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic (onset group) and again after one year (one-year group).
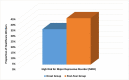
Results: A total of 422 HCWs were included (Mean (SD) age, 35.3 (9.9) years; 71.3% males), with 211 (50%) participants in each group. In the total cohort, the mean PHQ-9 score was 8.5, and 36.7% reported clinically significant levels of depressive symptoms with a PHQ-9 score of ≥10. Compared to the onset group, the one-year group reported a higher risk of major depressive disorder (41.7% vs. 31.8%; OR 1.538; 95%CI 1.032-2.291; p=0.034), a higher mean PHQ-9 score (9.5 (6.8) vs. 7.4 (5.3), p<0.001), and more severe depressive symptoms (p<0.005). Participants who were younger, unmarried, underwent testing for COVID-19, reported lower monthly income, did not receive special COVID-19 education, or had lower satisfaction with institutional preparedness had significantly higher depression scores and symptoms in both onset and one-year groups (p<0.05 for each category). Female gender and direct contact with COVID-19 patients or samples were significant risk factors within the onset group. Occupation as a physician, history of COVID-19 testing or infection, and perception of significant changes in work schedule or intensity were significantly associated with higher depression scores and symptoms among the one-year group.
Conclusion: This study sheds light on an unspoken but significant rise in prevalence estimates and severity of depressive symptoms among HCWs over a year of the COVID-19 pandemic and shows the vulnerable subgroups for whom a psychological intervention might be warranted.
Keywords: COVID-19; Depression; Health providers; Healthcare workers; One-year; Physicians.
© 2022 Al Yassin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures

References
-
- Chriscaden K. Impact of COVID-19 on people’s livelihoods, their health and our food systems. World Heal. Organ. 2020 https://www.who.int/news/item/13-10-2020-impact-of-COVID-19-on-people’s-...
-
- Allain-Dupré D., Chatry I., Kornprobst A. The territorial impact of COVID-19: Managing the crisis across levels of government. Available from: https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/the-territorial-impact...
-
- Andersen A.J., Mary-Krause M., Bustamante J.J.H., Héron M., El Aarbaoui T., Melchior M. Symptoms of anxiety/depression during the COVID-19 pandemic and associated lockdown in the community: longitudinal data from the TEMPO cohort in France. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03383-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohut M. Global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic: 1 year on. Med. News Today. 2021 Available from: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/global-impact-of-the-COVID-19-... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
