Trigeminal Schwannoma - Case Report of a Rare Tumour
- PMID: 37274992
- PMCID: PMC10235234
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-022-03405-6
Trigeminal Schwannoma - Case Report of a Rare Tumour
Abstract
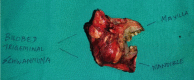
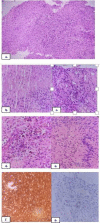
Schwannomas are benign nerve tumours arising from the Schwann cells. Approximately 25-45% of schwannomas occurs in the head and neck region. Majority of schwannomas in the head and neck region arise from the vagus nerve. Trigeminal schwannomas account for about 0.2% of all intracranial tumours. Trigeminal schwannomas can originate from any section of the fifth cranial nerve, from the root to the distal extracranial branches, but majority develops from the Gasserian ganglion, usually growing in the middle cranium. Most common presenting symptom is facial pain. MRI is the imaging modality of choice and CT scan usually serves as a supplementary imaging especially for skull base tumours. 47 year old male patient presented to the outpatient department with complains of swelling over the left side of palate. Contrast enhanced CT scan demonstrated a large bilobed heterogeneously enhancing soft tissue lesion in the left infratemporal fossa with widened foramen ovale and extension of lesion into the Meckel's cave, larger contiguous component extending into ramus of mandible. MRI scan showed a large lobulated mass in the left masticator space with intracranial extension. Biopsy of the lesion was suggestive of schwannoma. The patient underwent left composite resection with dural repair and free flap reconstruction. Post operatively, on day 5 he developed features of meningitis for which he was treated conservatively and later discharged in stable condition. Trigeminal schwannomas are rare tumours with very low chance of malignant transformation which commonly presents with facial pain. MRI is the imaging modality of choice. Complete surgical excision is the treatment of choice.
Keywords: Infratemporal fossa; Schwannoma; Trigeminal nerve.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2022. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNo potential conflict of interest relevant to this article exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Surgical management of trigeminal schwannomas: defining the role for endoscopic endonasal approaches.Neurosurg Focus. 2014;37(4):E17. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14341. Neurosurg Focus. 2014. PMID: 25270136
-
Trigeminal schwannoma.Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Jul-Dec;8(2):149-152. doi: 10.4103/njms.NJMS_82_14. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2017. PMID: 29386819 Free PMC article.
-
Microsurgical Resection of Trigeminal Schwannomas: 3-Dimensional Operative Video.Oper Neurosurg. 2020 Jan 1;18(1):E18. doi: 10.1093/ons/opz097. Oper Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31120116
-
Giant dumbbell-shaped middle cranial fossa trigeminal schwannoma with extension to the infratemporal and posterior fossae.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007;149(9):959-63; discussion 964. doi: 10.1007/s00701-007-1173-6. Epub 2007 May 29. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007. PMID: 17534571 Review.
-
Primary malignant lymphoma of the trigeminal region treated with rapid infusion of high-dose MTX and radiation: case report and review of the literature.Surg Neurol. 2003 Oct;60(4):343-8; discussion 348. doi: 10.1016/s0090-3019(02)01046-7. Surg Neurol. 2003. PMID: 14505860 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Anatomical Comparison of Surgical Approaches to Meckel's Cave.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 30;12(21):6847. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216847. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959312 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Transnasal Excision of Foramen Ovale Schwannoma: A Case Report and Literature Review.Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2025 Aug 8;2025:1152945. doi: 10.1155/crot/1152945. eCollection 2025. Case Rep Otolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40822612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Massimo Politi MD, Corrado Toro DMD, PhD MD, Massimo Sbuelz FEBOMS. A giant trigeminal schwannoma of the infratemporal fossa removed by transmandibular approach and coronoidectomy. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Cases. 2016;2:10–13. doi: 10.1016/j.omsc.2016.02.002. - DOI
-
- Verocay J. Zur Kenntnis der “neurofibrome”. Beitr Pathol Anat. 1910;48:1.
-
- Schisano G, Olivecrona H (1960) : Neurinomas of the Gasserian ganglion and trigeminal root. J Neurosurg. 17:306–22.10.3171/jns.1960.17.2.0306 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
