Intratumour microbiome of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 37275446
- PMCID: PMC10237023
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i5.713
Intratumour microbiome of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
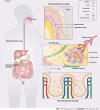
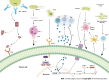
Pancreatic cancer is a high mortality malignancy with almost equal mortality and morbidity rates. Both normal and tumour tissues of the pancreas were previously considered sterile. In recent years, with the development of technologies for high-throughput sequencing, a variety of studies have revealed that pancreatic cancer tissues contain small amounts of bacteria and fungi. The intratumour microbiome is being revealed as an influential contributor to carcinogenesis. The intratumour microbiome has been identified as a crucial factor for pancreatic cancer progression, diagnosis, and treatment, chemotherapy resistance, and immune response. A better understanding of the biology of the intratumour microbiome of pancreatic cancer contributes to the establishment of better early cancer screening and treatment strategies. This review focuses on the possible origins of the intratumour microbiome in pancreatic cancer, the intratumour localization, the interaction with the tumour microenvironment, and strategies for improving the outcome of pancreatic cancer treatment. Thus, this review offers new perspectives for improving the prognosis of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Chemoresistance; Diagnosis; Intratumour microbiome; Pancreatic cancer; Prognosis; Tumour microenvironment.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Mizrahi JD, Surana R, Valle JW, Shroff RT. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2020;395:2008–2020. - PubMed
-
- Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Bäckhed F. From Dietary Fiber to Host Physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Key Bacterial Metabolites. Cell. 2016;165:1332–1345. - PubMed
-
- Tilg H, Zmora N, Adolph TE, Elinav E. The intestinal microbiota fuelling metabolic inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:40–54. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

