Lytic granule exocytosis at immune synapses: lessons from neuronal synapses
- PMID: 37275872
- PMCID: PMC10233144
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1177670
Lytic granule exocytosis at immune synapses: lessons from neuronal synapses
Abstract
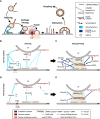
Regulated exocytosis is a central mechanism of cellular communication. It is not only the basis for neurotransmission and hormone release, but also plays an important role in the immune system for the release of cytokines and cytotoxic molecules. In cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), the formation of the immunological synapse is required for the delivery of the cytotoxic substances such as granzymes and perforin, which are stored in lytic granules and released via exocytosis. The molecular mechanisms of their fusion with the plasma membrane are only partially understood. In this review, we discuss the molecular players involved in the regulated exocytosis of CTL, highlighting the parallels and differences to neuronal synaptic transmission. Additionally, we examine the strengths and weaknesses of both systems to study exocytosis.
Keywords: CD8+ cells; SNARE proteins; cytotoxic T lymphocytes; endocytosis; exocytosis; neuron; synapse.
Copyright © 2023 Chang, Schirra, Pattu, Krause and Becherer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

