Potential of algae-derived alginate oligosaccharides and β-glucan to counter inflammation in adult zebrafish intestine
- PMID: 37275890
- PMCID: PMC10235609
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183701
Potential of algae-derived alginate oligosaccharides and β-glucan to counter inflammation in adult zebrafish intestine
Abstract
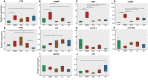
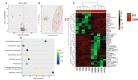
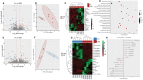
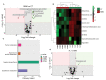
Alginate oligosaccharides (AOS) are natural bioactive compounds with anti-inflammatory properties. We performed a feeding trial employing a zebrafish (Danio rerio) model of soybean-induced intestinal inflammation. Five groups of fish were fed different diets: a control (CT) diet, a soybean meal (SBM) diet, a soybean meal+β-glucan (BG) diet and 2 soybean meal+AOS diets (alginate products differing in the content of low molecular weight fractions - AL, with 31% < 3kDa and AH, with 3% < 3kDa). We analyzed the intestinal transcriptomic and plasma metabolomic profiles of the study groups. In addition, we assessed the expression of inflammatory marker genes and histological alterations in the intestine. Dietary algal β-(1, 3)-glucan and AOS were able to bring the expression of certain inflammatory genes altered by dietary SBM to a level similar to that in the control group. Intestinal transcriptomic analysis indicated that dietary SBM changed the expression of genes linked to inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum, reproduction and cell motility. The AL diet suppressed the expression of genes related to complement activation, inflammatory and humoral response, which can likely have an inflammation alleviation effect. On the other hand, the AH diet reduced the expression of genes, causing an enrichment of negative regulation of immune system process. The BG diet suppressed several immune genes linked to the endopeptidase activity and proteolysis. The plasma metabolomic profile further revealed that dietary SBM can alter inflammation-linked metabolites such as itaconic acid, taurochenodeoxycholic acid and enriched the arginine biosynthesis pathway. The diet AL helped in elevating one of the short chain fatty acids, namely 2-hydroxybutyric acid while the BG diet increased the abundance of a vitamin, pantothenic acid. Histological evaluation revealed the advantage of the AL diet: it increased the goblet cell number and length of villi of the intestinal mucosa. Overall, our results indicate that dietary AOS with an appropriate amount of < 3kDa can stall the inflammatory responses in zebrafish.
Keywords: RNA seq; gut; macroalgae; metabolomics; microalgae; prebiotics; β-glucans.
Copyright © 2023 Rehman, Gora, Abdelhafiz, Dias, Pierre, Meynen, Fernandes, Sørensen, Brugman and Kiron.
Conflict of interest statement
Author JD was employed by company SPAROS Lda., RP by CEVA and KM by Kemin Aquascience. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME, Prescott SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, et al. . Expert consensus document: the international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol (2017) 14:491–502. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

