Measurement precision across cognitive domains in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) data set
- PMID: 37276134
- PMCID: PMC10247161
- DOI: 10.1037/neu0000901
Measurement precision across cognitive domains in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) data set
Abstract
Objective: To demonstrate measurement precision of cognitive domains in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) data set.
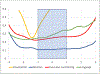
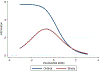
Method: Participants with normal cognition (NC), mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and Alzheimer's disease (AD) were included from all ADNI waves. We used data from each person's last study visit to calibrate scores for memory, executive function, language, and visuospatial functioning. We extracted item information functions for each domain and used these to calculate standard errors of measurement. We derived scores for each domain for each diagnostic group and plotted standard errors of measurement for the observed range of scores.
Results: Across all waves, there were 961 people with NC, 825 people with MCI, and 694 people with AD at their most recent study visit (data pulled February 25, 2019). Across ADNI's battery there were 34 memory items, 18 executive function items, 20 language items, and seven visuospatial items. Scores for each domain were highest on average for people with NC, intermediate for people with MCI, and lowest for people with AD, with most scores across all groups in the range of -1 to +1. Standard error of measurement in the range from -1 to +1 was highest for memory, intermediate for language and executive functioning, and lowest for visuospatial.
Conclusion: Modern psychometric approaches provide tools to help understand measurement precision of the scales used in studies. In ADNI, there are important differences in measurement precision across cognitive domains. (PsycInfo Database Record (c) 2023 APA, all rights reserved).
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


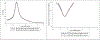
References
-
- Chapman LJ, & Chapman JP (1973). Disordered thought in schizophrenia. NY: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
-
- Chapman LJ, & Chapman JP (1978). Measurement of differential deficits. J Psychiatr Res, 14, 303–311. - PubMed

