Development and evaluation of helper dependent adenoviral vectors for inner ear gene delivery
- PMID: 37276687
- PMCID: PMC10427999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2023.108819
Development and evaluation of helper dependent adenoviral vectors for inner ear gene delivery
Abstract
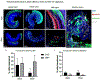
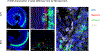
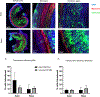
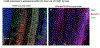
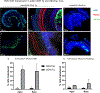
Viral vector gene therapy is an attractive strategy to treat hearing loss. Since hearing loss is due to a variety of pathogenic signaling cascades in distinct cells, viral vectors that can express large or multiple genes in a cell-type specific manner are needed. Helper-dependent adenoviral vectors (HdAd) are safe viral vectors with a large packaging capacity (-36 kb). Despite the potential of HdAd, its use in the inner ear is largely unexplored. Therefore, to evaluate the utility of HdAd for inner ear gene therapy, we created two HdAd vectors that use distinct cellular receptors for transduction: HdAd Serotype Type 5 (HdAd5), the Coxsackie-Adenovirus Receptor (CAR) and a chimeric HdAd 5/35, the human CD46+ receptor (hCD46). We delivered these vectors through the round window (RW) or scala media in CBA/J, C57Bl6/J and hCD46 transgenic mice. Immunostaining in conjunction with confocal microscopy of cochlear sections revealed that multiple cell types were transduced using HdAd5 and HdAd 5/35 in all mouse models. Delivery of HdAd5 via RW in the C57Bl/6 J or CBA/J cochlea resulted in transduced mesenchymal cells of the peri‑lymphatic lining and modiolar region while scala media delivery resulted in transduction of supporting cells and inner hair cells. Hd5/35 transduction was CD46 dependent and RW delivery of HdAd5/35 in the hCD46 mouse model resulted in a similar transduction pattern as HdAd5 in the peri‑lymphatic lining and modiolar region in the cochlea. Our data indicate that HdAd vectors are promising vectors for use in inner ear gene therapy to treat some causes of hearing loss.
Keywords: Gene therapy; Hearing loss; Helper dependent adenovirus; Inner ear.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helper-dependent adenovirus-mediated gene transfer into the adult mouse cochlea.Otol Neurotol. 2007 Dec;28(8):1100-8. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e318158973f. Otol Neurotol. 2007. PMID: 18043435
-
Targeted Integration and High-Level Transgene Expression in AAVS1 Transgenic Mice after In Vivo HSC Transduction with HDAd5/35++ Vectors.Mol Ther. 2019 Dec 4;27(12):2195-2212. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.08.006. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Mol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31494053 Free PMC article.
-
Use of helper-dependent adenoviral vectors of alternative serotypes permits repeat vector administration.Gene Ther. 1999 Sep;6(9):1565-73. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3300995. Gene Ther. 1999. PMID: 10490766
-
Gene therapy with helper-dependent adenoviral vectors: lessons from studies in large animal models.Virus Genes. 2017 Oct;53(5):684-691. doi: 10.1007/s11262-017-1471-x. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Virus Genes. 2017. PMID: 28593513 Review.
-
Gene therapy in the inner ear using adenovirus vectors.Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;66:37-51. doi: 10.1159/000218206. Epub 2009 Jun 2. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 2009. PMID: 19494571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in cochlear gene therapies.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2023 Dec 1;35(6):631-640. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000001273. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37417821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cochlear diffusion from the cerebrospinal fluid space with gadolinium contrast.Mol Ther. 2023 Sep 6;31(9):2566-2569. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.08.001. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37582360 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Treatment following Triple-AAV Delivery in Mature Murine Model of Human CDH23-Associated Hearing Loss.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Nov 24;45(12):9413-9421. doi: 10.3390/cimb45120590. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38132436 Free PMC article.
-
AAV-mediated transgene delivery targeting spiral ganglion nonsensory cells.Neuroreport. 2025 Jun 4;36(9):497-503. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000002172. Epub 2025 May 14. Neuroreport. 2025. PMID: 40377965 Free PMC article.
-
CaV 2.1 α1 subunit motifs that control presynaptic CaV 2.1 subtype abundance are distinct from CaV 2.1 preference.J Physiol. 2024 Feb;602(3):485-506. doi: 10.1113/JP284957. Epub 2023 Dec 28. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38155373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dabdoub A, Fritzsch B, Popper AN, Fay RR, SpringerLink (Online service). The Primary Auditory Neurons of the Mammalian Cochlea Available from: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3031-9. - DOI
-
- Mowry SE, Woodson E, Gantz BJ. New frontiers in cochlear implantation: acoustic plus electric hearing, hearing preservation, and more. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2012;45(1):187–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

