Prehospital stroke-scale machine-learning model predicts the need for surgical intervention
- PMID: 37277424
- PMCID: PMC10241931
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36004-8
Prehospital stroke-scale machine-learning model predicts the need for surgical intervention
Abstract
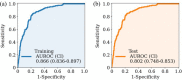
While the development of prehospital diagnosis scales has been reported in various regions, we have also developed a scale to predict stroke type using machine learning. In the present study, we aimed to assess for the first time a scale that predicts the need for surgical intervention across stroke types, including subarachnoid haemorrhage and intracerebral haemorrhage. A multicentre retrospective study was conducted within a secondary medical care area. Twenty-three items, including vitals and neurological symptoms, were analysed in adult patients suspected of having a stroke by paramedics. The primary outcome was a binary classification model for predicting surgical intervention based on eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost). Of the 1143 patients enrolled, 765 (70%) were used as the training cohort, and 378 (30%) were used as the test cohort. The XGBoost model predicted stroke requiring surgical intervention with high accuracy in the test cohort, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.802 (sensitivity 0.748, specificity 0.853). We found that simple survey items, such as the level of consciousness, vital signs, sudden headache, and speech abnormalities were the most significant variables for accurate prediction. This algorithm can be useful for prehospital stroke management, which is crucial for better patient outcomes.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TN and YY (Yamao) are inventors and have submitted patents related to this work. TN and YY (Yamao) serve as directors and hold shares in Smart119 Inc. REM serves as a chief scientist in Smart119 Inc. The remaining authors have disclosed that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

