Molecular mechanisms of gasdermin D pore-forming activity
- PMID: 37277654
- PMCID: PMC12379974
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-023-01526-w
Molecular mechanisms of gasdermin D pore-forming activity
Abstract
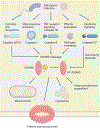
The regulated disruption of the plasma membrane, which can promote cell death, cytokine secretion or both is central to organismal health. The protein gasdermin D (GSDMD) is a key player in this process. GSDMD forms membrane pores that can promote cytolysis and the release of interleukin-1 family cytokines into the extracellular space. Recent discoveries have revealed biochemical and cell biological mechanisms that control GSDMD pore-forming activity and its diverse downstream immunological effects. Here, we review these multifaceted regulatory activities, including mechanisms of GSDMD activation by proteolytic cleavage, dynamics of pore assembly, regulation of GSDMD activities by posttranslational modifications, membrane repair and the interplay of GSDMD and mitochondria. We also address recent insights into the evolution of the gasdermin family and their activities in species across the kingdoms of life. In doing so, we hope to condense recent progress and inform future studies in this rapidly moving field in immunology.
© 2023. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
J.C.K. consults and holds equity in Corner Therapeutics, Larkspur Biosciences and Neumora Therapeutics. None of these relationships influenced this study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

