Amino acid metabolism in immune cells: essential regulators of the effector functions, and promising opportunities to enhance cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 37277776
- PMCID: PMC10240810
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-023-01453-1
Amino acid metabolism in immune cells: essential regulators of the effector functions, and promising opportunities to enhance cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
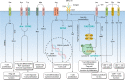
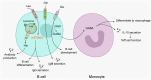
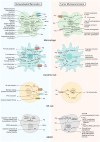
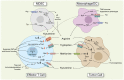
Amino acids are basic nutrients for immune cells during organ development, tissue homeostasis, and the immune response. Regarding metabolic reprogramming in the tumor microenvironment, dysregulation of amino acid consumption in immune cells is an important underlying mechanism leading to impaired anti-tumor immunity. Emerging studies have revealed that altered amino acid metabolism is tightly linked to tumor outgrowth, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance through governing the fate of various immune cells. During these processes, the concentration of free amino acids, their membrane bound transporters, key metabolic enzymes, and sensors such as mTOR and GCN2 play critical roles in controlling immune cell differentiation and function. As such, anti-cancer immune responses could be enhanced by supplement of specific essential amino acids, or targeting the metabolic enzymes or their sensors, thereby developing novel adjuvant immune therapeutic modalities. To further dissect metabolic regulation of anti-tumor immunity, this review summarizes the regulatory mechanisms governing reprogramming of amino acid metabolism and their effects on the phenotypes and functions of tumor-infiltrating immune cells to propose novel approaches that could be exploited to rewire amino acid metabolism and enhance cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: Amino acids; Immune cells; SLC transporters; Tumor microenvironment; mTOR.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no potential conflicts of interest in this review.
Figures
References
-
- Roy DG, Kaymak I, Williams KS, Ma EH, Jones RG. Immunometabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Ann Rev Cancer Biol. 2021;5:137–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030518-055817. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

