Speaking the host language: how Salmonella effector proteins manipulate the host
- PMID: 37279149
- PMCID: PMC10333799
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001342
Speaking the host language: how Salmonella effector proteins manipulate the host
Abstract
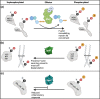
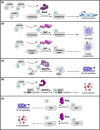
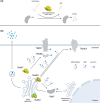
Salmonella injects over 40 virulence factors, termed effectors, into host cells to subvert diverse host cellular processes. Of these 40 Salmonella effectors, at least 25 have been described as mediating eukaryotic-like, biochemical post-translational modifications (PTMs) of host proteins, altering the outcome of infection. The downstream changes mediated by an effector's enzymatic activity range from highly specific to multifunctional, and altogether their combined action impacts the function of an impressive array of host cellular processes, including signal transduction, membrane trafficking, and both innate and adaptive immune responses. Salmonella and related Gram-negative pathogens have been a rich resource for the discovery of unique enzymatic activities, expanding our understanding of host signalling networks, bacterial pathogenesis as well as basic biochemistry. In this review, we provide an up-to-date assessment of host manipulation mediated by the Salmonella type III secretion system injectosome, exploring the cellular effects of diverse effector activities with a particular focus on PTMs and the implications for infection outcomes. We also highlight activities and functions of numerous effectors that remain poorly characterized.
Keywords: Salmonella pathogenesis; biochemical mechanism; intracellular pathogen; post-translational modification; type III effector protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Holohan N, Wallat M, Hai Yen Luu T, Clark E, Truong DTQ, et al. Analysis of antimicrobial resistance in non-typhoidal Salmonella collected from pork retail outlets and slaughterhouses in Vietnam using whole genome sequencing. Front Vet Sci. 2022;9:816279. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.816279. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

