The impact of cell-based therapy on female sexual dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37279578
- PMCID: PMC12017765
- DOI: 10.1093/sxmrev/qead023
The impact of cell-based therapy on female sexual dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Female sexual dysfunction (FSD) is a complex issue affecting women of all ages; it involves several overlapping body systems and profoundly affects quality of life. The use of cell-based therapy, such as mesenchymal stem cells, has recently been investigated as a potential treatment for FSD.
Objectives: This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to assess FSD outcomes following cell-based therapy.
Methods: We evaluated peer-reviewed articles from multiple online databases through November 2022 to identify studies that used cell-based therapy and reported sexual function outcomes in women. We performed a meta-analysis using data pooled from 3 clinical trials at our institution: CRATUS (NCT02065245), ACESO (NCT02886884), and CERES (NCT03059355). All 3 trials collected data from the Sexual Quality of Life-Female (SQOL-F) questionnaire as an exploratory outcome.
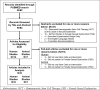
Results: Existing literature on this topic is scarce. Five clinical studies and 1 animal study were included in the systematic review, and only 2 clinical studies were considered good quality: 1 reported significant SQOL-F improvement in women 6 months after cell therapy, and 1 reported posttherapy sexual satisfaction in all women. When individual patient data were pooled in a meta-analysis from 29 women across 3 trials at our institution, the SQOL-F was not significantly improved.
Conclusion: Despite growing interest in cell-based therapy for women's sexual health, this important issue is understudied in the literature. The optimal route, source, and dose of cell therapy to produce clinically meaningful change have yet to be determined, and further research is needed in larger randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials.
Keywords: cell-based therapy; female sexual dysfunction; mesenchymal stem cells; regenerative medicine; restorative therapy; stem cell therapy.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The International Society of Sexual Medicine. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Parish SJ, Cottler-Casanova S, Clayton AH, McCabe MP, Coleman E, Reed GM. The evolution of the female sexual disorder/dysfunction definitions, nomenclature, and classifications: a review of DSM, ICSM, ISSWSH, and ICD. Sex Med Rev. 2021;9(1):36–56. - PubMed
-
- Parish SJ, Hahn SR, Goldstein SW, et al. The International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health process of care for the identification of sexual concerns and problems in women. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(5):842–856. - PubMed
-
- McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Atalla E, et al. Definitions of sexual dysfunctions in women and men: a consensus statement from the Fourth International Consultation on Sexual Medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13(2):135–143. - PubMed
-
- Derogatis LR, Komer L, Katz M, et al. Treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder in premenopausal women: efficacy of flibanserin in the VIOLET study. J Sex Med. 2012;9(4):1074–1085. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical