Cadmium effects on net N2O production by the deep-sea isolate Shewanella loihica PV-4
- PMID: 37279908
- PMCID: PMC10337742
- DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fnad047
Cadmium effects on net N2O production by the deep-sea isolate Shewanella loihica PV-4
Abstract
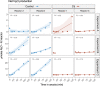
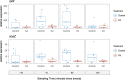
Deep-sea mining may lead to the release of high concentrations of metals into the surrounding seabed, which can disturb important ecosystem functions provided by microbial communities. Among these, the production of N2O and its reduction to N2 is of great relevance since N2O is an important greenhouse gas. Metal impacts on net N2O production by deep-sea bacteria are, however, currently unexplored. Here, we evaluated the effects of cadmium (Cd) on net N2O production by a deep-sea isolate, Shewanella loihica PV-4. We performed a series of Cd exposure incubations in oxic conditions and determined N2O fluxes during induced anoxic conditions, as well as the relative expression of the nitrite reductase gene (nirK), preceding N2O production, and N2O reductase gene (nosZ), responsible for N2O reduction. Net N2O production by S. loihica PV-4 exposed to Cd was strongly inhibited when compared to the control treatment (no metal). Both nirK and nosZ gene expression were inhibited in reactors with Cd, but nirK inhibition was stronger, supporting the lower net N2O production observed with Cd. The Cd inhibition of net N2O production observed in this study poses the question whether other deep-sea bacteria would undergo the same effects. Future studies should address this question as well as its applicability to complex communities and other physicochemical conditions, which remain to be evaluated.
Keywords: deep-sea; denitrification; gene expression; metal contamination; mining; nitrous oxide.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dissimilatory Nitrate Reduction to Ammonium (DNRA) and Denitrification Pathways Are Leveraged by Cyclic AMP Receptor Protein (CRP) Paralogues Based on Electron Donor/Acceptor Limitation in Shewanella loihica PV-4.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Jan 4;87(2):e01964-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01964-20. Print 2021 Jan 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33158888 Free PMC article.
-
pH Control Enables Simultaneous Enhancement of Nitrogen Retention and N2O Reduction in Shewanella loihica Strain PV-4.Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 20;8:1820. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01820. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28979255 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrite Control over Dissimilatory Nitrate/Nitrite Reduction Pathways in Shewanella loihica Strain PV-4.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 May 15;81(10):3510-7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00688-15. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25769828 Free PMC article.
-
Grazing exclusion alters denitrification N2O/(N2O + N2) ratio in alpine meadow of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Feb 20;912:169358. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169358. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38135064
-
Nitrous Oxide Reduction Kinetics Distinguish Bacteria Harboring Clade I NosZ from Those Harboring Clade II NosZ.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016 Jun 13;82(13):3793-800. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00409-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27084012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afzal M, Yu M, Tang Cet al. . The negative impact of cadmium on nitrogen transformation processes in a paddy soil is greater under non-flooding than flooding conditions. Environ Int. 2019;129:451–60. - PubMed
-
- Bange HW, Arévalo-Martínez DL, de la PMet al. . A harmonized nitrous oxide (N 2 O) ocean observation network for the 21st century. Front Mar Sci. 2019;6:1–10. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00157. - PubMed
-
- Baptista MS, Miller RJ, Halewood ERet al. . Impacts of silver nanoparticles on a natural Estuarine Plankton community. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49:12968–74. - PubMed
-
- Behera M, Dandapat J, Rath CC. Effect of heavy metals on growth response and antioxidant defense protection in Bacillus cereus. J Basic Microbiol. 2014;54:1201–9. - PubMed
-
- Broman E, Motwani NH, Bonaglia Set al. . Denitrification responses to increasing cadmium exposure in Baltic Sea sediments. Aquat Toxicol. 2019;217:105328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

