Super enhancers targeting ZBTB16 in osteogenesis protect against osteoporosis
- PMID: 37280207
- PMCID: PMC10244438
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-023-00267-8
Super enhancers targeting ZBTB16 in osteogenesis protect against osteoporosis
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Super enhancers targeting ZBTB16 in osteogenesis protect against osteoporosis.Bone Res. 2023 Jun 26;11(1):33. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00275-8. Bone Res. 2023. PMID: 37365159 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
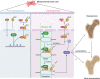
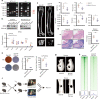
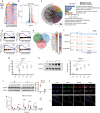
As the major cell precursors in osteogenesis, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are indispensable for bone homeostasis and development. However, the primary mechanisms regulating osteogenic differentiation are controversial. Composed of multiple constituent enhancers, super enhancers (SEs) are powerful cis-regulatory elements that identify genes that ensure sequential differentiation. The present study demonstrated that SEs were indispensable for MSC osteogenesis and involved in osteoporosis development. Through integrated analysis, we identified the most common SE-targeted and osteoporosis-related osteogenic gene, ZBTB16. ZBTB16, positively regulated by SEs, promoted MSC osteogenesis but was expressed at lower levels in osteoporosis. Mechanistically, SEs recruited bromodomain containing 4 (BRD4) at the site of ZBTB16, which then bound to RNA polymerase II-associated protein 2 (RPAP2) that transported RNA polymerase II (POL II) into the nucleus. The subsequent synergistic regulation of POL II carboxyterminal domain (CTD) phosphorylation by BRD4 and RPAP2 initiated ZBTB16 transcriptional elongation, which facilitated MSC osteogenesis via the key osteogenic transcription factor SP7. Bone-targeting ZBTB16 overexpression had a therapeutic effect on the decreased bone density and remodeling capacity of Brd4fl/fl Prx1-cre mice and osteoporosis (OP) models. Therefore, our study shows that SEs orchestrate the osteogenesis of MSCs by targeting ZBTB16 expression, which provides an attractive focus and therapeutic target for osteoporosis. Without SEs located on osteogenic genes, BRD4 is not able to bind to osteogenic identity genes due to its closed structure before osteogenesis. During osteogenesis, histones on osteogenic identity genes are acetylated, and OB-gain SEs appear, enabling the binding of BRD4 to the osteogenic identity gene ZBTB16. RPAP2 transports RNA Pol II from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and guides Pol II to target ZBTB16 via recognition of the navigator BRD4 on SEs. After the binding of the RPAP2-Pol II complex to BRD4 on SEs, RPAP2 dephosphorylates Ser5 at the Pol II CTD to terminate the transcriptional pause, and BRD4 phosphorylates Ser2 at the Pol II CTD to initiate transcriptional elongation, which synergistically drives efficient transcription of ZBTB16, ensuring proper osteogenesis. Dysregulation of SE-mediated ZBTB16 expression leads to osteoporosis, and bone-targeting ZBTB16 overexpression is efficient in accelerating bone repair and treating osteoporosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

