Psychedelics promote plasticity by directly binding to BDNF receptor TrkB
- PMID: 37280397
- PMCID: PMC10244169
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01316-5
Psychedelics promote plasticity by directly binding to BDNF receptor TrkB
Abstract
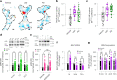
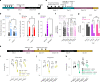
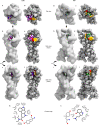
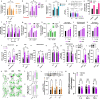
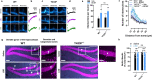
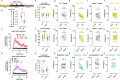
Psychedelics produce fast and persistent antidepressant effects and induce neuroplasticity resembling the effects of clinically approved antidepressants. We recently reported that pharmacologically diverse antidepressants, including fluoxetine and ketamine, act by binding to TrkB, the receptor for BDNF. Here we show that lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and psilocin directly bind to TrkB with affinities 1,000-fold higher than those for other antidepressants, and that psychedelics and antidepressants bind to distinct but partially overlapping sites within the transmembrane domain of TrkB dimers. The effects of psychedelics on neurotrophic signaling, plasticity and antidepressant-like behavior in mice depend on TrkB binding and promotion of endogenous BDNF signaling but are independent of serotonin 2A receptor (5-HT2A) activation, whereas LSD-induced head twitching is dependent on 5-HT2A and independent of TrkB binding. Our data confirm TrkB as a common primary target for antidepressants and suggest that high-affinity TrkB positive allosteric modulators lacking 5-HT2A activity may retain the antidepressant potential of psychedelics without hallucinogenic effects.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
R.M., M.G., C.B., G.E., I.V., P.C.C. and E.C. are inventors in a patent application filed by the University of Helsinki that is related to these findings (GB2210278.4). E.C. has received speaker fees from Janssen Cilag. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


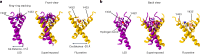






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

