Interleukin-24-mediated antitumor effects against human glioblastoma via upregulation of P38 MAPK and endogenous TRAIL-induced apoptosis and LC3-II activation-dependent autophagy
- PMID: 37280571
- PMCID: PMC10242982
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-11021-y
Interleukin-24-mediated antitumor effects against human glioblastoma via upregulation of P38 MAPK and endogenous TRAIL-induced apoptosis and LC3-II activation-dependent autophagy
Abstract
Background: Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7 (Mda-7) encodes IL-24, which can induce apoptosis in cancer cells. A novel gene therapy approach to treat deadly brain tumors, recombinant mda-7 adenovirus (Ad/mda-7) efficiently kills glioma cells. In this study, we investigated the factors affecting cell survival and apoptosis and autophagy mechanisms that destroy glioma cells by Ad/IL-24.
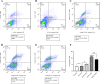
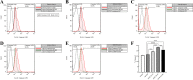
Methods: Human glioblastoma U87 cell line was exposed to a multiplicity of infections of Ad/IL-24. Antitumor activities of Ad/IL-24 were assessed by cell proliferation (MTT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release analysis. Using flow cytometry, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis were investigated. Using the ELISA method, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) level was determined as an apoptosis-promoting factor and Survivin level as an anti-apoptotic factor. The expression levels of TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand(TRAIL) and P38 MAPK genes were assessed by the Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction(RT‑qPCR) method. The expression levels of caspase-3 and protein light chain 3-II (LC3-II) proteins were analyzed by flow cytometry as intervening factors in the processes of apoptosis and autophagy in the cell death signaling pathway, respectively.
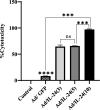
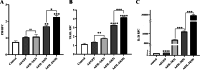
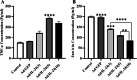
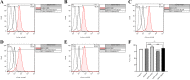
Results: The present findings demonstrated that transduction of IL-24 inhibited cell proliferation and induced cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in glioblastoma. Compared with cells of the control groups, Ad/IL24-infected U87 cells exhibited significantly increased elevated caspase-3, and TNF-α levels, while the survivin expression was decreased. TRAIL was shown to be upregulated in tumor cells after Ad/IL-24 infection and studies of the apoptotic cascade regulators indicate that Ad/IL-24 could further enhance the activation of apoptosis through the TNF family of death receptors. In the current study, we demonstrate that P38 MAPK is significantly activated by IL-24 expression. In addition, the overexpression of mda-7/IL-24 in GBM cells induced autophagy, which was triggered by the upregulation of LC3-II.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates the antitumor effect of IL-24 on glioblastoma and may be a promising therapeutic approach for GBM cancer gene therapy.
Keywords: Antitumor; Autophagy; Cell apoptosis; Glioblastoma; IL-24; Recombinant adenovirus.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 sensitizes TNF-α and TRAIL/Apo2L dependent cell death through upregulation of death receptors in human cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021 Jun;1868(7):119037. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2021.119037. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33839168
-
RND2 attenuates apoptosis and autophagy in glioblastoma cells by targeting the p38 MAPK signalling pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Aug 31;39(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01671-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32867814 Free PMC article.
-
Cisplatin-enhanced sensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme U251 cells to adenovirus-delivered TRAIL in vitro.Tumour Biol. 2010 Dec;31(6):613-22. doi: 10.1007/s13277-010-0077-x. Epub 2010 Jul 11. Tumour Biol. 2010. PMID: 20623264
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
Potential of Curcumin and Its Analogs in Glioblastoma Therapy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;14(3):351. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030351. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227413 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-24: A Multidimensional Therapeutic for Treatment of Human Diseases.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2025 May-Jun;17(3):e70013. doi: 10.1002/wnan.70013. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40338095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pectinose induces cell cycle arrest in luminal A and triple-negative breast cancer cells by promoting autophagy through activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2024 May 24;24(1):639. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12293-8. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38789954 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying TXNIP's anti-tumor role in breast cancer, including interaction with a novel, pro-tumor partner: CAST.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Apr 2;16(1):236. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07566-4. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40175348 Free PMC article.
-
D-arabinose induces cell cycle arrest by promoting autophagy via p38 MAPK signaling pathway in breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 May 16;14(1):11219. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61309-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38755221 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements and challenges in immunocytokines: A new arsenal against cancer.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Nov;14(11):4649-4664. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.07.024. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39664443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Juratli TA, Schackert G, Krex D. Current status of local therapy in malignant gliomas—a clinical review of three selected approaches. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;139(3):341–58. - PubMed
-
- Yahya EB, Alqadhi AM. Recent trends in cancer therapy: a review on the current state of gene delivery. Life Sci. 2021;269:119087. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

