The role of psychological distress, stigma and coping strategies on help-seeking intentions in a sample of Italian college students
- PMID: 37280661
- PMCID: PMC10243082
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-023-01171-w
The role of psychological distress, stigma and coping strategies on help-seeking intentions in a sample of Italian college students
Abstract
Background: Mental health issues are common among university students, but the latter are unlikely to seek professional help even when mental health services are available. Coping strategies, stigma and psychological distress are often considered as factors that can affect help-seeking intentions in university students.
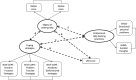
Methods: This study aimed to determine the role of coping strategies, stigma and psychological distress on the intentions to seek professional help for psychological problems. All students (N = 13,886) from an Italian medium-sized university were asked to participate in a multidimensional online survey and 3754 (27.1%) agreed to participate. A Structural Equation Modelling approach was applied to explore the simultaneous direct and indirect effects of distress, stigma and coping strategies on professional help-seeking intentions.
Results: Results showed that students were not very likely to seek professional help and, through the Structural Equation Model, psychological distress was found to be positively correlated with coping strategies, which in turn was negatively associated with the stigma of seeking help. The latter was negatively associated with professional help-seeking intentions. These effects suggest that students with significant psychological distress use coping strategies to face the stigma of seeking help: the lower the stigma of seeking help, the higher the chance of developing intentions to seek professional help.
Conclusions: This study suggests the importance of implementing programs to encourage college students to seek help, including measures that foster a stigma-free environment, reduce psychological distress and promote the use of adaptive coping strategies. Interventions should be focused firstly on self-stigma and secondly on perceived stigma, taking into consideration the level of psychological distress and social stereotypes associated with mental disorders and help seeking behaviours. Programs about coping are also essential and should focus on promoting emotion-focused strategies and problem-focused strategies.
Keywords: Coping strategies; Counselling; Help seeking behaviour; Psychological distress; Stigma; University students.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Thompson M, Pawson C, Evans B. Navigating entry into higher education: the transition to independent learning and living. J Furth High Educ. 2021;45(10):1398–1410. doi: 10.1080/0309877X.2021.1933400. - DOI
-
- Bruffaerts R, Mortier P, Auerbach RP, Alonso J, Hermosillo De la Torre AE, Cuijpers P, et al. Lifetime and 12-month treatment for mental disorders and suicidal thoughts and behaviors among first year college students. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 2019;28(2):e1764. doi: 10.1002/mpr.1764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 56, 27/09/2018/University of Brescia, Department of Clinical and Experimental Sciences
- 56, 27/09/2018/University of Brescia, Department of Clinical and Experimental Sciences
- 56, 27/09/2018/University of Brescia, Department of Clinical and Experimental Sciences
- 56, 27/09/2018/University of Brescia, Department of Clinical and Experimental Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

