Outcomes in Patients with High-Risk Features after Fixed-Duration Ibrutinib plus Venetoclax: Phase II CAPTIVATE Study in First-Line Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- PMID: 37282671
- PMCID: PMC10345960
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2779
Outcomes in Patients with High-Risk Features after Fixed-Duration Ibrutinib plus Venetoclax: Phase II CAPTIVATE Study in First-Line Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
Purpose: The CAPTIVATE study investigated first-line ibrutinib plus venetoclax for chronic lymphocytic leukemia in 2 cohorts: minimal residual disease (MRD)-guided randomized discontinuation (MRD cohort) and Fixed Duration (FD cohort). We report outcomes of fixed-duration ibrutinib plus venetoclax in patients with high-risk genomic features [del(17p), TP53 mutation, and/or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGHV)] in CAPTIVATE.
Patients and methods: Patients received three cycles of ibrutinib 420 mg/day then 12 cycles of ibrutinib plus venetoclax (5-week ramp-up to 400 mg/day). FD cohort patients (n = 159) received no further treatment. Forty-three MRD cohort patients with confirmed undetectable MRD (uMRD) after 12 cycles of ibrutinib plus venetoclax received randomized placebo treatment.
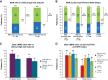
Results: Of 195 patients with known status of genomic risk features at baseline, 129 (66%) had ≥1 high-risk feature. Overall response rates were >95% regardless of high-risk features. In patients with and without high-risk features, respectively, complete response (CR) rates were 61% and 53%; best uMRD rates: 88% and 70% (peripheral blood) and 72% and 61% (bone marrow); 36-month progression-free survival (PFS) rates: 88% and 92%. In subsets with del(17p)/TP53 mutation (n = 29) and unmutated IGHV without del(17p)/TP53 mutation (n = 100), respectively, CR rates were 52% and 64%; uMRD rates: 83% and 90% (peripheral blood) and 45% and 80% (bone marrow); 36-month PFS rates: 81% and 90%. Thirty-six-month overall survival (OS) rates were >95% regardless of high-risk features.
Conclusions: Deep, durable responses and sustained PFS seen with fixed-duration ibrutinib plus venetoclax are maintained in patients with high-risk genomic features, with similar PFS and OS to those without high-risk features. See related commentary by Rogers, p. 2561.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

Comment on
-
A CAPTIVATEing Analysis for Higher-Risk CLL.Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 14;29(14):2561-2562. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-0807. Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37289004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imbruvica (ibrutinib) [package insert]. South San Francisco, CA: Pharmacyclics LLC; 2020.
-
- VENCLEXTA (venetoclax tablets) for oral use [package insert]. South San Francisco, CA: Genentech USA, Inc; 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

