Clinical and Prognostic Factors in Patients with IgG4-Related Kidney Disease
- PMID: 37283461
- PMCID: PMC10564355
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000193
Clinical and Prognostic Factors in Patients with IgG4-Related Kidney Disease
Abstract
Background: IgG4-related kidney disease is a major manifestation of IgG4-related disease, a systemic fibroinflammatory disorder. However, the clinical and prognostic kidney-related factors in patients with IgG4-related kidney disease are insufficiently defined.
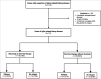
Methods: We conducted an observational cohort study using data from 35 sites in two European countries. Clinical, biologic, imaging, and histopathologic data; treatment modalities; and outcomes were collected from medical records. Logistic regression was performed to identify the possible factors related to an eGFR ≤30 ml/min per 1.73 m 2 at the last follow-up. Cox proportional hazards model was performed to assess the factors associated with the risk of relapse.
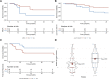
Results: We studied 101 adult patients with IgG4-related disease with a median follow-up of 24 (11-58) months. Of these, 87 (86%) patients were male, and the median age was 68 (57-76) years. Eighty-three (82%) patients had IgG4-related kidney disease confirmed by kidney biopsy, with all biopsies showing tubulointerstitial involvement and 16 showing glomerular lesions. Ninety (89%) patients were treated with corticosteroids, and 18 (18%) patients received rituximab as first-line therapy. At the last follow-up, the eGFR was below 30 ml/min per 1.73 m 2 in 32% of patients; 34 (34%) patients experienced a relapse, while 12 (13%) patients had died. By Cox survival analysis, the number of organs involved (hazard ratio [HR], 1.26; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 1.55) and low C3 and C4 concentrations (HR, 2.31; 95% CI, 1.10 to 4.85) were independently associated with a higher risk of relapse, whereas first-line therapy with rituximab was protective (HR, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.06 to 0.78). At their last follow-up, 19 (19%) patients had an eGFR ≤30 ml/min per 1.73 m 2 . Age (odd ratio [OR], 1.11; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.20), peak serum creatinine (OR, 2.74; 95% CI, 1.71 to 5.47), and serum IgG4 level ≥5 g/L (OR, 4.46; 95% CI, 1.23 to 19.40) were independently predictive for severe CKD.
Conclusions: IgG4-related kidney disease predominantly affected middle-aged men and manifested as tubulointerstitial nephritis with potential glomerular involvement. Complement consumption and the number of organs involved were associated with a higher relapse rate, whereas first-line therapy with rituximab was associated with lower relapse rate. Patients with high serum IgG4 concentrations (≥5 g/L) had more severe kidney disease.
Copyright © 2023 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
V. Audard reports consultancy for, honoraria from, and advisory or leadership roles on Advisory boards for Addmedica, Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Vifor pharma. J.J. Boffa reports consultancy for AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Otsuka, Travere, and Vifor pharma; honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Otsuka, and Vifor pharma; and advisory or leadership roles for AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Otsuka, Travere, and Vifor pharma. J. Chemouny reports consultancy for AstraZeneca. A. Devresse reports consultancy for and advisory or leadership roles for Alnylam Pharmaceuticals and Merck. S. Duquennoy reports employment with Fondation AUB SANTE. J.M. Halimi reports consultancy for Alexion, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim France, Servier, and Vifor Fresenius; research funding from AstraZeneca; and honoraria from Alexion, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim France, MSD, Sanofi, Servier, and Vifor. D. Joly reports honoraria from AstraZeneca and Bayer. A. Karras reports consultancy for Alnylam, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Otsuka, Vifor; honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bohringer-Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, and Vifor; advisory or leadership roles for Novartis, Otsuka, and Vifor; and speakers bureau for AstraZeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Otsuka, Pfizer, and Vifor. A. Mathian reports consultancy for AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Otsuka; honoraria from AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, and Otsuka; advisory or leadership role for AstraZeneca; and speakers bureau for AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, and Otsuka. L. Mercadal reports honoraria for Congress travel and hotel in France and reports advisory or leadership roles for nephrologie thérapeutique review board and Société francophone de néphrologie dialyse transplantation. J. Olagne reports serving on speakers bureau for GlaxoSmithKline. S. Palat reports employment with and advisory or leadership role for Janssen Cilag. E. Plaisier reports employment with AURA PARIS. O. Thaunat reports consultancy for AstraZeneca, Biotest, and Novartis; research funding from bioMérieux, BMS, and Immucor; honoraria from Astellas, Biotest, and Novartis; and advisory or leadership role for ESOT. E. Vilaine reports consultancy for and honoraria from AstraZeneca. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Comment in
-
IgG4-Related Kidney Disease.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023 Aug 1;18(8):994-996. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000235. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37418275 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

