Basic fibroblast growth factor induces proliferation and collagen production by fibroblasts derived from the bovine corpus luteum†
- PMID: 37283496
- PMCID: PMC10502575
- DOI: 10.1093/biolre/ioad065
Basic fibroblast growth factor induces proliferation and collagen production by fibroblasts derived from the bovine corpus luteum†
Abstract
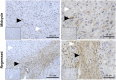
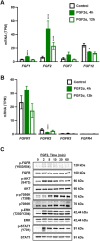
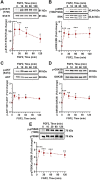
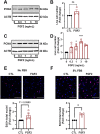
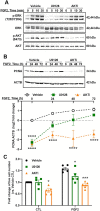
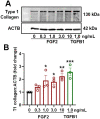
Cyclic regression of the ovarian corpus luteum, the endocrine gland responsible for progesterone production, involves rapid matrix remodeling. Despite fibroblasts in other systems being known for producing and maintaining extracellular matrix, little is known about fibroblasts in the functional or regressing corpus luteum. Vast transcriptomic changes occur in the regressing corpus luteum, among which are reduced levels of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and increased expression of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) after 4 and 12 h of induced regression, when progesterone is declining and the microvasculature is destabilizing. We hypothesized that FGF2 activates luteal fibroblasts. Analysis of transcriptomic changes during induced luteal regression revealed elevations in markers of fibroblast activation and fibrosis, including fibroblast activation protein (FAP), serpin family E member 1 (SERPINE1), and secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1). To test our hypothesis, we treated bovine luteal fibroblasts with FGF2 to measure downstream signaling, type 1 collagen production, and proliferation. We observed rapid and robust phosphorylation of various signaling pathways involved in proliferation, such as ERK, AKT, and STAT1. From our longer-term treatments, we determined that FGF2 has a concentration-dependent collagen-inducing effect, and that FGF2 acts as a mitogen for luteal fibroblasts. FGF2-induced proliferation was greatly blunted by inhibition of AKT or STAT1 signaling. Our results suggest that luteal fibroblasts are responsive to factors that are released by the regressing bovine corpus luteum, an insight into the contribution of fibroblasts to the microenvironment in the regressing corpus luteum.
Keywords: PGF2α; corpus luteum; fibroblast; fibroblast growth factor; fibrosis; luteolysis.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for the Study of Reproduction 2023.
Figures


References
-
- Stocco C, Telleria C, Gibori G. The molecular control of corpus luteum formation, function, and regression. Endocr Rev 2007; 28:117–149. - PubMed
-
- Van Linthout S, Miteva K, Tschöpe C. Crosstalk between fibroblasts and inflammatory cells. Cardiovasc Res 2014; 102:258–269. - PubMed
-
- Gospodarowicz D, Cheng J, Lui G, Baird A, Esch F, Bohlen P. Corpus luteum angiogenic factor is related to fibroblast growth factor. Endocrinology 1985; 117:2383–2391. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita H, Kamada D, Shirasuna K, Matsui M, Shimizu T, Kida K, Berisha B, Schams D, Miyamoto A. Effect of local neutralization of basic fibroblast growth factor or vascular endothelial growth factor by a specific antibody on the development of the corpus luteum in the cow. Mol Reprod Dev 2008; 75:1449–1456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

