Fusion of the molecular adjuvant C3d to cleavage-independent native-like HIV-1 Env trimers improves the elicited antibody response
- PMID: 37283743
- PMCID: PMC10239957
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1180959
Fusion of the molecular adjuvant C3d to cleavage-independent native-like HIV-1 Env trimers improves the elicited antibody response
Abstract
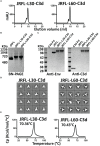
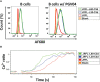
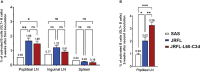
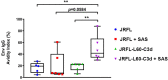
An effective HIV vaccine likely requires the elicitation of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) against multiple HIV-1 clades. The recently developed cleavage-independent native flexibly linked (NFL) envelope (Env) trimers exhibit well-ordered conformation and elicit autologous tier 2 NAbs in multiple animal models. Here, we investigated whether the fusion of molecular adjuvant C3d to the Env trimers can improve B- cell germinal center (GC) formation and antibody responses. To generate Env-C3d trimers, we performed a glycine-serine- based (G4S) flexible peptide linker screening and identified a linker range that allowed native folding. A 30-60- amino- acid- long linker facilitates Env-to-C3d association and achieves the secretion of well-ordered trimers and the structural integrity and functional integrity of Env and C3d. The fusion of C3d did not dramatically affect the antigenicity of the Env trimers and enhanced the ability of the Env trimers to engage and activate B cells in vitro. In mice, the fusion of C3d enhanced germinal center formation, the magnitude of Env-specific binding antibodies, and the avidity of the antibodies in the presence of an adjuvant. The Sigma Adjuvant System (SAS) did not affect the trimer integrity in vitro but contributed to altered immunogenicity in vivo, resulting in increased tier 1 neutralization, likely by increased exposure of variable region 3 (V3). Taken together, the results indicate that the fusion of the molecular adjuvant, C3d, to the Env trimers improves antibody responses and could be useful for Env-based vaccines against HIV.
Keywords: C3d; HIV-1; immunogenicity; molecular adjuvant; vaccine.
Copyright © 2023 Bale, Yang, Alirezaei, Wilson, Ota, Doyle, Cottrell, Guenaga, Tran, Li, Stamatatos, Nemazee, Ward and Wyatt.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors JG, KT, and RTW are/were employed by IAVI. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Sanders RW, Derking R, Cupo A, Julien JP, Yasmeen A, de Val N, et al. . A next-generation cleaved, soluble hiv-1 env trimer, Bg505 Sosip.664 Gp140, expresses multiple epitopes for broadly neutralizing but not non-neutralizing antibodies. PloS Pathog (2013) 9(9):e1003618. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003618 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

