The emerging roles and mechanism of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications in urologic tumours progression
- PMID: 37284313
- PMCID: PMC10239868
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1192495
The emerging roles and mechanism of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications in urologic tumours progression
Abstract
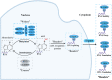
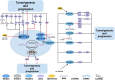
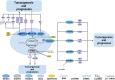
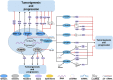
Prostate cancer (PCa), bladder cancer (BC), and renal cell cancer (RCC) are the most common urologic tumours in males. N6-methyladenosine (m6A), adenosine N6 methylation, is the most prevalent RNA modification in mammals. Increasing evidence suggests that m6A plays a crucial role in cancer development. In this review, we comprehensively analyzed the influence of m6A methylation on Prostate cancer, bladder cancer, and renal cell cancer and the relationship between the expression of relevant regulatory factors and their development and occurrence, which provides new insights and approaches for the early clinical diagnosis and targeted therapy of urologic malignancies.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; coding RNAs; epitranscriptome; non-coding RNAs; posttranscriptional modification; urologic tumours.
Copyright © 2023 Zhu, Zhao, Guan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Environmental exposures and RNA N6-Methyladenosine modified long Non-Coding RNAs.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020 Sep;50(8):641-649. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2020.1812511. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32924714 Review.
-
The Relationship Between the Network of Non-coding RNAs-Molecular Targets and N6-Methyladenosine Modification in Colorectal Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 6;9:772542. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.772542. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34938735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VIRMA-Dependent N6-Methyladenosine Modifications Regulate the Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs CCAT1 and CCAT2 in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 25;12(4):771. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040771. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32218194 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine RNA modification and its interaction with regulatory non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer.RNA Biol. 2021 Nov 12;18(sup2):551-561. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1974749. Epub 2021 Oct 21. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 34674600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New understandings of the genetic regulatory relationship between non-coding RNAs and m6A modification.Front Genet. 2023 Dec 6;14:1270983. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1270983. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 38125749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of N6‑methyladenosine in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2024 Jun;51(6):88. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8747. Epub 2024 May 17. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38757383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of NiCl2 Intake Through Respiratory Tract on Antioxidant Capacity, Lung, and Trace Element Content in Mice.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 May 17. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04630-0. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40381093
-
The m6A regulators in prostate cancer: molecular basis and clinical perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1448872. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1448872. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39268470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Basu H. S., Wilganowski N., Robertson S., Reuben J. M., Cohen E. N., Zurita A., et al. (2021). Prostate cancer cells survive anti-androgen and mitochondrial metabolic inhibitors by modulating glycolysis and mitochondrial metabolic activities. Prostate 81 (12), 799–811. 10.1002/pros.24146 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

