The emerging roles and mechanism of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications in urologic tumours progression
- PMID: 37284313
- PMCID: PMC10239868
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1192495
The emerging roles and mechanism of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications in urologic tumours progression
Abstract
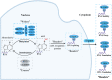
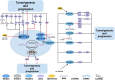
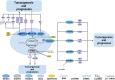
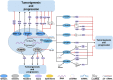
Prostate cancer (PCa), bladder cancer (BC), and renal cell cancer (RCC) are the most common urologic tumours in males. N6-methyladenosine (m6A), adenosine N6 methylation, is the most prevalent RNA modification in mammals. Increasing evidence suggests that m6A plays a crucial role in cancer development. In this review, we comprehensively analyzed the influence of m6A methylation on Prostate cancer, bladder cancer, and renal cell cancer and the relationship between the expression of relevant regulatory factors and their development and occurrence, which provides new insights and approaches for the early clinical diagnosis and targeted therapy of urologic malignancies.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; coding RNAs; epitranscriptome; non-coding RNAs; posttranscriptional modification; urologic tumours.
Copyright © 2023 Zhu, Zhao, Guan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Basu H. S., Wilganowski N., Robertson S., Reuben J. M., Cohen E. N., Zurita A., et al. (2021). Prostate cancer cells survive anti-androgen and mitochondrial metabolic inhibitors by modulating glycolysis and mitochondrial metabolic activities. Prostate 81 (12), 799–811. 10.1002/pros.24146 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

