What's a good prediction? Challenges in evaluating an agent's knowledge
- PMID: 37284424
- PMCID: PMC10240643
- DOI: 10.1177/10597123221095880
What's a good prediction? Challenges in evaluating an agent's knowledge
Abstract
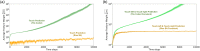
Constructing general knowledge by learning task-independent models of the world can help agents solve challenging problems. However, both constructing and evaluating such models remain an open challenge. The most common approaches to evaluating models is to assess their accuracy with respect to observable values. However, the prevailing reliance on estimator accuracy as a proxy for the usefulness of the knowledge has the potential to lead us astray. We demonstrate the conflict between accuracy and usefulness through a series of illustrative examples including both a thought experiment and an empirical example in Minecraft, using the General Value Function framework (GVF). Having identified challenges in assessing an agent's knowledge, we propose an alternate evaluation approach that arises naturally in the online continual learning setting: we recommend evaluation by examining internal learning processes, specifically the relevance of a GVF's features to the prediction task at hand. This paper contributes a first look into evaluation of predictions through their use, an integral component of predictive knowledge which is as of yet unexplored.
Keywords: Reinforcement learning; agent knowledge; general value functions.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures






References
-
- Barreto A., Dabney W., Munos R., Hunt J. J., Schaul T., van Hasselt H. P., Silver D. (2017). Successor features for transfer in reinforcement learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 30, 4055–4065.
-
- Comanici G., Precup D., Barreto A., Toyama D. K., Aygün E., Hamel P., Vezhnevets S., Hou S., Mourad S. (2018) Knowledge representation for reinforcement learning using general value functions. Technical report.
-
- Edwards A. L., Hebert J. S., Pilarski P. M. (2016). Machine learning and unlearning to autonomously switch between the functions of a myoelectric arm. In 2016 6th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Singapore, 26–29 June 2016 (pp. 514–521). Piscataway, NJ: IEEE. 10.1109/biorob.2016.7523678 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
