The effects of exercise on the quality of life of patients with breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on the QLQ-C30 quality of life scale
- PMID: 37284711
- PMCID: PMC10240433
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-23-126
The effects of exercise on the quality of life of patients with breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on the QLQ-C30 quality of life scale
Abstract
Background: Studies have reported that exercise can effectively improve the quality of life of breast cancer (BC) patients. However, considering the differences in exercise form and intensity, it is difficult to quantify and unify the improved outcomes, and there are contradictions in the conclusions. This meta-analysis aimed to quantitatively evaluate the effects of exercise on the quality of life (QoL) of patients with BC based on the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QoL Questionnaire-C30 (QLQ-C30) scale, to provide optimization suggestions for the treatment plan of BC survivors.
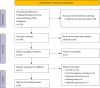
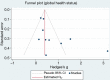
Methods: The literature were extracted from the databases of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Wanfang, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure. The main outcomes were extracted from the final included literature and chi square tests and I2 statistics were used to evaluate the heterogeneity among the included studies. Statistical analysis was performed by Stata/SE 16.0 software and Review Manager 5.4 software. The funnel plot was used to test for evaluation publication bias.
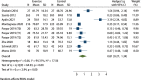
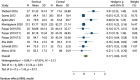
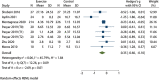
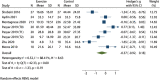
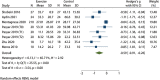
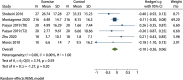
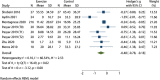
Results: All 8 included articles were original studies. The risk bias evaluation showed that 2 articles had low risk of bias and 6 articles had uncertain risk of bias. The results of meta-analysis revealed the following: (I) exercise significantly improved the overall health status of BC patients [mean difference (Hedges's g) =0.81, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.27, 1.34]; (II) exercise significantly improved the physiological function of patients (Hedges's g =0.78, 95% CI: 0.34, 1.22), daily life function (Hedges's g =0.45, 95% CI: 0.13, 0.77), emotional function (Hedges's g =0.52, 95% CI: 0.20, 0.84); (III) exercise significantly reduced the fatigue symptoms (Hedges's g =-0.51, 95% CI: -0.84, -0.19), nausea and vomiting symptoms (Hedges's g =-0.35, 95% CI: -0.60, -0.10), insomnia symptoms (Hedges's g =-0.59, 95% CI: -0.91, -0.26), and economic difficulties (Hedges's g =-0.48, 95% CI: -0.78, -0.18) of patients.
Conclusions: Exercise can significantly improve the overall physical health and body functions of BC survivors. Exercise can also significantly reduce the symptoms of fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and insomnia in BC patients. Different levels of exercise have significant effects on improving the quality of life of BC survivors, which is worth being widely advocated.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Quality of Life Questionnaire-C30 scale (QLQ-C30 scale); exercise; quality of life (QoL).
2023 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-23-126/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Impact of spiritual interventions in individuals with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2024 Aug;71:102646. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2024.102646. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38943773
-
The effect of exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields on cognitive performance in human experimental studies: Systematic review and meta-analyses.Environ Int. 2024 Sep;191:108899. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108899. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 39265322
-
Health-related quality of life in breast cancer patients in Asia: A meta-analysis and systematic review.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;12:954179. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.954179. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36249065 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Chinese traditional ethnic sports on sleep quality among the elderly: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PeerJ. 2025 Feb 21;13:e19019. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19019. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 39995989 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of yoga on clinical symptoms, quality of life and social functioning in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Asian J Psychiatr. 2024 Mar;93:103959. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2024.103959. Epub 2024 Feb 4. Asian J Psychiatr. 2024. PMID: 38342034
Cited by
-
Association between quality of life and mortality risk in patients with breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer. 2024 Jul;31(4):552-561. doi: 10.1007/s12282-024-01581-7. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38592636
-
Exercise Therapy in Oncology—the Impact on Quality of Life and Side Effects.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024 May 17;121(10):331-337. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2024.0038. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024. PMID: 38509786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An assessment of study characteristics, quality and reporting in cancer prehabilitation literature: a scoping review.BMJ Open. 2025 Jul 11;15(7):e093832. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093832. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40645637 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation Exercises Supported by Monitor-Augmented Reality for Patients with High-Grade Glioma Undergoing Radiotherapy: Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 29;12(21):6838. doi: 10.3390/jcm12216838. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37959303 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Aerobic and Resistance Training Improves Body Composition, Alters Cardiometabolic Risk, and Ameliorates Cancer-Related Indicators in Breast Cancer Patients and Survivors with Overweight/Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Sports Sci Med. 2024 Jun 1;23(2):366-395. doi: 10.52082/jssm.2024.366. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Sports Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38841642 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
